Three-dimensional model of a substrate-bound SARS chymotrypsin-like cysteine proteinase predicted by multiple molecular dynamics simulations: catalytic efficiency regulated by substrate binding
- PMID: 15690493
- PMCID: PMC7167676
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.20249
Three-dimensional model of a substrate-bound SARS chymotrypsin-like cysteine proteinase predicted by multiple molecular dynamics simulations: catalytic efficiency regulated by substrate binding
Erratum in
- Proteins. 2006 May 15;63(3):716
Abstract
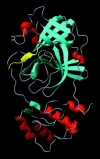
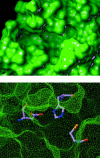
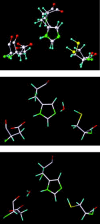
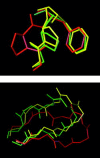
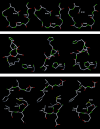
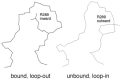
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a contagious and deadly disease caused by a new coronavirus. The protein sequence of the chymotrypsin-like cysteine proteinase (CCP) responsible for SARS viral replication has been identified as a target for developing anti-SARS drugs. Here, I report the ATVRLQ(p1)A(p1')-bound CCP 3D model predicted by 420 different molecular dynamics simulations (2.0 ns for each simulation with a 1.0-fs time step). This theoretical model was released at the Protein Data Bank (PDB; code: 1P76) before the release of the first X-ray structure of CCP (PDB code: 1Q2W). In contrast to the catalytic dyad observed in X-ray structures of CCP and other coronavirus cysteine proteinases, a catalytic triad comprising Asp187, His41, and Cys145 is found in the theoretical model of the substrate-bound CCP. The simulations of the CCP complex suggest that substrate binding leads to the displacement of a water molecule entrapped by Asp187 and His41, thus converting the dyad to a more efficient catalytic triad. The CCP complex structure has an expanded active-site pocket that is useful for anti-SARS drug design. In addition, this work demonstrates that multiple molecular dynamics simulations are effective in correcting errors that result from low-sequence-identity homology modeling.
Copyright 2004 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Marra MA, Jones SJM, Astell CR, Holt RA, Brooks‐Wilson A, Butterfield YSN, Khattra J, Asano JK, Barber SA, Chan SY, et al. The genome sequence of the SARS‐associated coronavirus. Science 2003; 300: 1399–1404. - PubMed
-
- Rota PA, Oberste MS, Monroe SS, Nix WA, Campagnoli R, Icenogle JP, Penaranda S, Bankamp B, Maher K, Chen MH, et al. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science 2003; 300: 1394–1399. - PubMed
-
- Anand K, Ziebuhr J, Wadhwani P, Mesters JR, Hilgenfeld R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti‐SARS drugs. Science 2003; 300: 1763–1767. - PubMed
-
- Xiong B, Gui C‐S, Xu X‐Y, Luo C, Chen J, Luo H‐B, Chen L‐L, Li G‐W, Sun T, Yu C‐Y, et al. A 3D model of SARS‐CoV 3CL proteinse and its inhibitors design by virtual screening. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2003; 24: 497–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

