Differential effects of ERK and p38 signaling in BMP-2 stimulated hypertrophy of cultured chick sternal chondrocytes
- PMID: 15691373
- PMCID: PMC548678
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-3-3
Differential effects of ERK and p38 signaling in BMP-2 stimulated hypertrophy of cultured chick sternal chondrocytes
Abstract
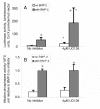
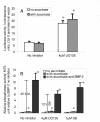
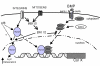
BACKGROUND: During endochondral bone formation, the hypertrophy of chondrocytes is accompanied by selective expression of several genes including type X collagen and alkaline phosphatase. This expression is stimulated by inducers including BMPs and ascorbate. A 316 base pair region of the type X collagen (Col X) promoter has been previously characterized as the site required for BMP regulation. The intent of this study was to examine the role of Mitogen Activated Protein (MAP) and related kinase pathways in the regulation of Col X transcription and alkaline phosphatase activity in pre-hypertrophic chick chondrocytes. RESULTS: Using a luciferase reporter regulated by the BMP-responsive region of the type X collagen promoter, we show that promoter activity is increased by inhibition of extra-cellular signal regulated kinases 1 or 2 (ERK1/2). In contrast the ability of BMP-2 to induce alkaline phosphatase activity is little affected by ERK1/2 inhibition. The previously demonstrated stimulatory affect of p38 on Col X was shown to act specifically at the BMP responsive region of the promoter. The inhibitory effect of the ERK1/2 pathway and stimulatory effect of the p38 pathway on the Col X promoter were confirmed by the use of mutant kinases. Inhibition of upstream kinases: protein kinase C (PKC) and phosphatidylinositol 3-(PI3) kinase pathways increased basal Col X activity but had no effect on the BMP-2 induced increase. In contrast, ascorbate had no effect on the BMP-2 responsive region of the Col X promoter nor did it alter the increase in promoter activity induced by ERK1/2 inhibition. The previously shown increase in alkaline phosphatase activity induced by ascorbate was not affected by any kinase inhibitors examined. However some reduction in the alkaline phosphatase activity induced by the combination of BMP-2 and ascorbate was observed with ERK1/2 inhibition. CONCLUSION: Our results demonstrate that ERK1/2 plays a negative role while p38 plays a positive role in the BMP-2 activated transcription of type X collagen. This regulation occurs specifically at the BMP-2 responsive promoter region of Col X. Ascorbate does not modulate Col X at this region indicating that BMP-2 and ascorbate exert their action on chondrocyte hypertrophy via different transcriptional pathways. MAP kinases seem to have only a modest effect on alkaline phosphatase when activity is induced by the combination of both BMP-2 and ascorbate.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A BMP responsive transcriptional region in the chicken type X collagen gene.J Bone Miner Res. 1998 Oct;13(10):1521-9. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.10.1521. J Bone Miner Res. 1998. PMID: 9783540
-
Rapid chondrocyte maturation by serum-free culture with BMP-2 and ascorbic acid.J Cell Biochem. 1997 Sep 1;66(3):394-403. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4644(19970901)66:3<394::aid-jcb11>3.0.co;2-f. J Cell Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9257195
-
Stimulation of type-X collagen gene transcription by retinoids occurs in part through the BMP signaling pathway.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 3:29-33. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200300003-00006. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003. PMID: 12925606
-
Retinoid signaling regulates CTGF expression in hypertrophic chondrocytes with differential involvement of MAP kinases.J Bone Miner Res. 2005 May;20(5):867-77. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.041235. Epub 2004 Dec 27. J Bone Miner Res. 2005. PMID: 15824860
-
Smad-Runx interactions during chondrocyte maturation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 1):S15-22. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11263661 Review.
Cited by
-
Osteogenic induction of asiatic acid derivatives in human periodontal ligament stem cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 29;13(1):14102. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41388-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37644086 Free PMC article.
-
A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Dovitinib (TKI-258), Enhances BMP-2-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation In Vitro.Mol Cells. 2016 May 31;39(5):389-94. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.2300. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Mol Cells. 2016. PMID: 27025387 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Cells Differentiation: How CFTR Mutations May Rule the Game of Stem Cells Commitment?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 7;9:611921. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.611921. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34026749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMP canonical Smad signaling through Smad1 and Smad5 is required for endochondral bone formation.Development. 2009 Apr;136(7):1093-104. doi: 10.1242/dev.029926. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Development. 2009. PMID: 19224984 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of BMP2 signaling in domains on the plasma membrane.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Jul;227(7):2880-8. doi: 10.1002/jcp.23032. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21938723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leboy PS, Vaias L, Uschmann B, Golub E, Adams SL, Pacifici M. Ascorbic-Acid Induces Alkaline-Phosphatase, Type-X Collagen, and Calcium Deposition in Cultured Chick Chondrocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1989;264:17281–17286. - PubMed
-
- Volk SW, Luvalle P, Leask T, Leboy PS. A BMP responsive transcriptional region in the chicken type X collagen gene. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 1998;13:1521–1529. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

