Global gene expression in neuroendocrine tumors from patients with the MEN1 syndrome
- PMID: 15691381
- PMCID: PMC549185
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-4-9
Global gene expression in neuroendocrine tumors from patients with the MEN1 syndrome
Abstract
Background: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1, OMIM 131100) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by endocrine tumors of the parathyroids, pancreatic islets and pituitary. The disease is caused by the functional loss of the tumor suppressor protein menin, coded by the MEN1 gene. The protein sequence has no significant homology to known consensus motifs. In vitro studies have shown menin binding to JunD, Pem, Smad3, NF-kappaB, nm23H1, and RPA2 proteins. However, none of these binding studies have led to a convincing theory of how loss-of-menin leads to neoplasia.
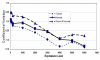
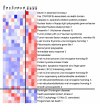
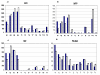
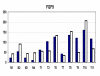
Results: Global gene expression studies on eight neuroendocrine tumors from MEN1 patients and 4 normal islet controls was performed utilizing Affymetrix U95Av2 chips. Overall hierarchical clustering placed all tumors in one group separate from the group of normal islets. Within the group of tumors, those of the same type were mostly clustered together. The clustering analysis also revealed 19 apoptosis-related genes that were under-expressed in the group of tumors. There were 193 genes that were increased/decreased by at least 2-fold in the tumors relative to the normal islets and that had a t-test significance value of p < or = 0.005. Forty-five of these genes were increased and 148 were decreased in the tumors relative to the controls. One hundred and four of the genes could be classified as being involved in cell growth, cell death, or signal transduction. The results from 11 genes were selected for validation by quantitative RT-PCR. The average correlation coefficient was 0.655 (range 0.235-0.964).
Conclusion: This is the first analysis of global gene expression in MEN1-associated neuroendocrine tumors. Many genes were identified which were differentially expressed in neuroendocrine tumors arising in patients with the MEN1 syndrome, as compared with normal human islet cells. The expression of a group of apoptosis-related genes was significantly suppressed, suggesting that these genes may play crucial roles in tumorigenesis in this syndrome. We identified a number of genes which are attractive candidates for further investigation into the mechanisms by which menin loss causes tumors in pancreatic islets. Of particular interest are: FGF9 which may stimulate the growth of prostate cancer, brain cancer and endometrium; and IER3 (IEX-1), PHLDA2 (TSS3), IAPP (amylin), and SST, all of which may play roles in apoptosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Accelerated proliferation and differential global gene expression in pancreatic islets of five-week-old heterozygous Men1 mice: Men1 is a haploinsufficient suppressor.Endocrinology. 2012 Jun;153(6):2588-98. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1924. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22492302
-
Global expression profiling of murine MEN1-associated tumors reveals a regulatory role for menin in transcription, cell cycle and chromatin remodelling.Int J Cancer. 2007 Aug 15;121(4):776-83. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22734. Int J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17455252
-
Mechanisms of disease: multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1-relation to chromatin modifications and transcription regulation.Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Oct;2(10):562-70. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0292. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 17024155 Review.
-
Dynamic epigenetic regulation by menin during pancreatic islet tumor formation.Mol Cancer Res. 2015 Apr;13(4):689-98. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0457. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25537453
-
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms in Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 14;22(8):4041. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084041. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of lncRNAs in pancreatic beta cell identity and diabetes susceptibility.Front Genet. 2014 Jul 1;5:193. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00193. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25071823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUNX1T1: a novel predictor of liver metastasis in primary pancreatic endocrine neoplasms.Pancreas. 2011 May;40(4):627-33. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182152bda. Pancreas. 2011. PMID: 21499216 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of small bowel and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors by gene-expression profiling.Surgery. 2012 Dec;152(6):998-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.08.040. Surgery. 2012. PMID: 23158174 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate early gene-X1 interferes with 26 S proteasome activity by attenuating expression of the 19 S proteasomal components S5a/Rpn10 and S1/Rpn2.Biochem J. 2007 Mar 1;402(2):367-75. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061072. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17107344 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2010 Nov 18;2(4):1901-10. doi: 10.3390/cancers2041901. Cancers (Basel). 2010. PMID: 24281208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marx SJ, Agarwal SK, Kester MB, Heppner C, Kim YS, Skarulis MC, James LA, Goldsmith PK, Saggar SK, Park SY, Spiegel AM, Burns AL, Debelenko LV, Zhuang Z, Lubensky IA, Liotta LA, Emmert-Buck MR, Guru SC, Manickam P, Crabtree J, Erdos MR, Collins FS, Chandrasekharappa SC. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1: clinical and genetic features of the hereditary endocrine neoplasias. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1999;54:397–438; discussion 438-9. - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekharappa SC, Guru SC, Manickam P, Olufemi SE, Collins FS, Emmert-Buck MR, Debelenko LV, Zhuang Z, Lubensky IA, Liotta LA, Crabtree JS, Wang Y, Roe BA, Weisemann J, Boguski MS, Agarwal SK, Kester MB, Kim YS, Heppner C, Dong Q, Spiegel AM, Burns AL, Marx SJ. Positional cloning of the gene for multiple endocrine neoplasia-type 1. Science. 1997;276:404–407. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5311.404. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

