Anterior chamber width measurement by high-speed optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 15691557
- PMCID: PMC1784115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.09.019
Anterior chamber width measurement by high-speed optical coherence tomography
Abstract
Objective: To measure anterior chamber (AC) width and other dimensions relevant to the sizing of phakic intraocular lenses (IOLs) with a high-speed optical coherence tomography (OCT) system.
Design: Cross-sectional observational study.
Participants: Both eyes of 20 normal volunteers.
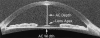
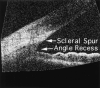
Methods: A novel high-speed (4000 axial scans/second) OCT prototype was developed for anterior segment scanning. The system uses long wavelength (1310 nm) for deeper angle penetration, rectangular scanning for undistorted imaging, and short image acquisition time (0.125 seconds) to reduce motion error. Three horizontal cross-sectional OCT images (15.5 mm wide and 6 mm deep) of the anterior segment were obtained from each eye with real-time image display to guide centration on the corneal apex. Image processing software was developed to correct for image warping resulting from index transitions. Anterior chamber dimensions were measured using computer calipers by 3 expert raters (ophthalmologists). Analysis of variance was used to determine interrater, interimage, right versus left eye, and intersubject standard deviation (SD) of OCT measurements.
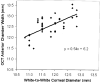
Main outcome measures: Anterior chamber width (recess to recess), AC depth, and crystalline lens vault as measured by OCT; external white-to-white (WTW) corneal diameter (CD) as measured by Holladay-Godwin gauge.
Results: The mean AC width was 12.53+/-0.47 mm (intereye SD), and the mean corneal diameter was 11.78+/-0.57 mm. Optical coherence tomography measurement of AC width has good repeatability from image to image (SD, 0.134 mm), but there was significant difference between raters (SD, 0.215 mm). Estimation of AC width from WTW CD by linear regression was relatively inaccurate (residual SD, 0.41 mm). The mean AC depth was 2.99+/-0.323 mm (intereye SD), with repeatability of less than 0.001 mm (interimage SD), and the mean crystalline lens vault was 0.39+/-0.27 mm with 0.023 mm repeatability.
Conclusions: Reproducible OCT AC biometry was demonstrated using a high-speed OCT prototype. Further improvement in reproducibility may be achieved by automating the measurements with a computer. Direct OCT AC width measurement may improve sizing of angle-supported AC IOLs over conventional estimation by WTW CD. The measurement of AC depth and lens vault also may be useful for other types of phakic AC IOLs.
Figures
Comment in
-
Anterior chamber width measurement.Ophthalmology. 2005 Sep;112(9):1638-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.03.005. Ophthalmology. 2005. PMID: 16139672 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Internal anterior chamber diameter using optical coherence tomography compared with white-to-white distances using automated measurements.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006 Nov;32(11):1809-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2006.08.023. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006. PMID: 17081862
-
Measurement of the internal diameter and depth of the anterior chamber: IOLMaster versus anterior chamber optical coherence tomographer.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005 Sep;31(9):1722-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.02.030. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005. PMID: 16246775
-
Fully automated biometry of in situ intraocular lenses using long scan depth spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.Eye Contact Lens. 2014 Jan;40(1):37-45. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000005. Eye Contact Lens. 2014. PMID: 24335453
-
Ocular biometry with swept-source optical coherence tomography.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2021 Jun 1;47(6):802-814. doi: 10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000000551. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2021. PMID: 33315731 Review.
-
Recent advances in ophthalmic anterior segment imaging: a new era for ophthalmic diagnosis?Br J Ophthalmol. 2007 Apr;91(4):551-7. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2006.103408. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 17372341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of central corneal thickness and anterior chamber depth measurements using three imaging technologies in normal eyes and after phakic intraocular lens implantation.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009 Aug;247(8):1139-46. doi: 10.1007/s00417-009-1086-6. Epub 2009 Apr 30. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19404662 Free PMC article.
-
Lens-vault analysis and its correlation with other biometric parameters using swept-source OCT.J Optom. 2022 Jan-Mar;15(1):88-99. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 Nov 1. J Optom. 2022. PMID: 34736867 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of angle-to-angle distance and corneal diameter in pediatric eyes using ultrasound biomicroscopy.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 18;19(6):e0305624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305624. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38889111 Free PMC article.
-
Imagery - ultrasound biomicroscopy and anterior segment Optical Coherence Tomography - in the diagnosis of anterior segment pathology.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2020 Jul-Sep;64(3):292-298. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33367163 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of anterior segment optical tomography parameters measured using a semi-automatic software to standard clinical instruments.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 4;8(6):e65559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065559. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23750265 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- O’Brien TP, Awwad ST. Phakic intraocular lenses and refractory lensectomy for myopia. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002;13:264–70. - PubMed
-
- Budo C, Hessloehl JC, Izak M, et al. Multicenter study of the Artisan phakic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:1163–71. - PubMed
-
- Menezo JL, Cisneros AL, Rodriguez-Salvador V. Endothelial study of iris-claw phakic lens: four year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998;24:1039–49. - PubMed
-
- Arne JL, Lesueur LC. Phakic posterior chamber lenses for high myopia: functional and anatomical outcomes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:369–74. - PubMed
-
- Alio JL, de la Hoz F, Ruiz-Moreno JM, Salem TF. Cataract surgery in highly myopic eyes corrected by phakic anterior chamber angle-supported lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:1303–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

