RNA-polymerase-I-directed rDNA transcription, life and works
- PMID: 15691654
- PMCID: PMC3858833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.12.008
RNA-polymerase-I-directed rDNA transcription, life and works
Abstract
In the extensive network of interdependent biochemical processes required for cell growth and division, there is mounting evidence that ribosomal DNA transcription by RNA polymerase I (pol I) not only drives cell growth via its direct role in production of the ribosomal RNA (rRNA) component of the protein-synthesis machinery, but that it is also crucial in determining the fate of the cell. Considerable progress has been made in recent years towards understanding both the function of components of the pol I transcription machinery and how cells accomplish the tight control of pol I transcription, balancing the supply of rRNA with demand under different growth conditions.
Figures

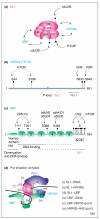

References
-
- Grummt I. Life on a planet of its own: regulation of RNA polymerase I transcription in the nucleolus. Genes Dev. 2003;17:1691–1702. - PubMed
-
- Moss T, Stefanovsky VY. At the center of eukaryotic life. Cell. 2002;109:545–548. - PubMed
-
- Reeder RH. Regulation of RNA polymerase I transcription in yeast and vertebrates. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1999;62:293–327. - PubMed
-
- Hannan KM, et al. Transcription by RNA polymerase I. Front. Biosci. 1998;3:d376–d398. - PubMed
-
- Comai L. Mechanism of RNA polymerase I transcription. Adv. Protein Chem. 2004;67:123–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

