Metabolically independent and accurately adjustable Aspergillus sp. expression system
- PMID: 15691916
- PMCID: PMC546773
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.2.672-678.2005
Metabolically independent and accurately adjustable Aspergillus sp. expression system
Abstract
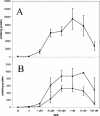
Filamentous fungi are well-established expression hosts often used to produce extracellular proteins of use in the food and pharmaceutical industries. The expression systems presently used in Aspergillus species rely on either strong constitutive promoters, e.g., that for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, or inducible systems derived from metabolic pathways, e.g., glaA (glucoamylase) or alc (alcohol dehydrogenase). We describe for Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus niger a novel expression system that utilizes the transcriptional activation of the human estrogen receptor by estrogenic substances. The system functions independently from metabolic signals and therefore can be used with low-cost, complex media. A combination of positive and negative regulatory elements in the promoter drives the expression of a reporter gene, yielding a linear dose response to the inducer. The off status is completely tight, yet the system responds within minutes to induction and reaches a level of expression of up to 15% of total cell protein after 8 h. Both Aspergillus species are very sensitive to estrogenic substances, and low-cost inducers function in the picomolar concentration range, at which estrogenic substances also can be found in the environment. Given this high sensitivity to estrogens, Aspergillus cells carrying estrogen-responsive units could be used to detect xenoestrogens in food or in the environment.
Figures


References
-
- Aravindakshan, J., M. Gregory, D. J. Marcogliese, M. Fournier, and D. G. Cyr. 2004. Consumption of xenoestrogen-contaminated fish during lactation alters adult male reproductive function. Toxicol. Sci. 81:179-189. - PubMed
-
- Archer, D. B., and J. F. Peberdy. 1997. The molecular biology of secreted enzyme production by fungi. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 17:273-306. - PubMed
-
- Belfroid, A. C., A. Van der Horst, A. D. Vethaak, A. J. Schafer, G. B. Rijs, J. Wegener, and W. P. Cofino. 1999. Analysis and occurrence of estrogenic hormones and their glucuronides in surface water and waste water in The Netherlands. Sci. Total Environ. 225:101-108. - PubMed
-
- Burger, G., J. Strauss, C. Scazzocchio, and B. F. Lang. 1991. nirA, the pathway-specific regulatory gene of nitrate assimilation in Aspergillus nidulans, encodes a putative GAL4-type zinc finger protein and contains four introns in highly conserved regions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:5746-5755. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

