Application of the BPEC pathway for large-scale biotechnological production of poly(3-mercaptopropionate) by recombinant Escherichia coli, including a novel in situ isolation method
- PMID: 15691938
- PMCID: PMC546776
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.2.835-841.2005
Application of the BPEC pathway for large-scale biotechnological production of poly(3-mercaptopropionate) by recombinant Escherichia coli, including a novel in situ isolation method
Abstract
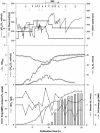
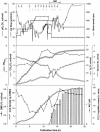
Metabolically engineered Escherichia coli JM109 harboring plasmid pBPP1 and expressing the nonnatural BPEC pathway for synthesis of thermoplastic polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) and novel polythioesters (PTE) to provide suitable substrates of PHA synthase was investigated with respect to biotechnological production of poly(3-mercaptopropionate) [poly(3MP)]. Fed-batch fermentation processes were established at the 30- and 500-liter scales in stirred tank bioreactors to produce kilogram amounts of poly(3MP). Cultivation was done in a modified M9 mineral salts medium containing glucose or glycerol as the carbon and energy source and with 3-mercaptopropionic acid (3MP) as the precursor substrate for poly(3MP) biosynthesis provided from the late exponential growth phase. Approximately 23 g of cell dry matter (CDM) per liter and poly(3MP) cell contents of up to 45% (wt/wt) were the highest cell densities and polymer contents obtained, respectively. At best, 69.1% (wt/wt) of 3MP was converted into poly(3MP), indicating that 3MP was mostly used for poly(3MP) biosynthesis. Furthermore, a novel in situ process for rapid and convenient isolation of poly(3MP) from the cells in the bioreactor was developed. This was achieved by addition of sodium dodecyl sulfate to the cultivation broth immediately after the fermentation, heating to 90 degrees C for 20 min with intensive stirring, and subsequent washing steps. The purity of such in situ isolated poly(3MP) was more than 98%, as revealed by gas chromatographic and elemental sulfur analyses of the material isolated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heat-shock protein HspA mimics the function of phasins sensu stricto in recombinant strains of Escherichia coli accumulating polythioesters or polyhydroxyalkanoates.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Feb;153(Pt 2):366-374. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.29260-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17259608
-
Biosynthesis of poly (3-mercaptopropionate) and poly (3-mercaptopropionate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate) with recombinant Escherichia coli.Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2003 Mar;19(2):195-9. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 15966321
-
Novel precursor substrates for polythioesters (PTE) and limits of PTE biosynthesis in Ralstonia eutropha.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003 Apr 25;221(2):191-6. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00185-X. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12725926
-
Effects of pH of fermentation medium on biosynthesis of poly[(3-hydroxybutyrate)-co-(3-mercaptopropionate)] by Wautersia eutropha.Macromol Biosci. 2006 Oct 20;6(10):818-26. doi: 10.1002/mabi.200600133. Macromol Biosci. 2006. PMID: 17022093
-
Hyperproduction of poly(4-hydroxybutyrate) from glucose by recombinant Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2012 May 2;11:54. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-11-54. Microb Cell Fact. 2012. PMID: 22550959 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases of Advenella mimigardefordensis and Ralstonia eutropha catalyze cleavage of 3,3'-dithiodipropionic acid into 3-mercaptopropionic acid.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Nov;76(21):7023-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01706-10. Epub 2010 Sep 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20833784 Free PMC article.
-
Succinyl-CoA:3-sulfinopropionate CoA-transferase from Variovorax paradoxus strain TBEA6, a novel member of the class III coenzyme A (CoA)-transferase family.J Bacteriol. 2013 Aug;195(16):3761-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.00456-13. Epub 2013 Jun 14. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23772073 Free PMC article.
-
Novel pathway for catabolism of the organic sulfur compound 3,3'-dithiodipropionic acid via 3-mercaptopropionic acid and 3-Sulfinopropionic acid to propionyl-coenzyme A by the aerobic bacterium Tetrathiobacter mimigardefordensis strain DPN7.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Jul;74(13):4028-35. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00422-08. Epub 2008 May 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18456849 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled autolysis facilitates the polyhydroxyalkanoate recovery in Pseudomonas putida KT2440.Microb Biotechnol. 2011 Jul;4(4):533-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2011.00257.x. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Microb Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21418544 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradation of the organic disulfide 4,4'-dithiodibutyric acid by Rhodococcus spp.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Dec;81(24):8294-306. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02059-15. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26407888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battley, E. H. 1991. Calculation of the heat of growth of Escherichia coli K-12 on succinic acid. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 37:334-343. - PubMed
-
- Fischer, F. 2002. 3-Mercaptopropionic acid (3MPA). Synlett 8:1368-1369.
-
- Good, C. A., H. Kramer, and M. Somogyi. 1933. The determination of glycogen. J. Biol. Chem. 100:485-491.
-
- Gresham, T. L., J. E. Jansen, F. W. Shaver., and J. T. Gregory. 1948. β-Propiolactone. II. Reactions with salts of inorganic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 70:998-999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

