PACS-2 controls endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria communication and Bid-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 15692567
- PMCID: PMC549619
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600559
PACS-2 controls endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria communication and Bid-mediated apoptosis
Erratum in
- EMBO J. 2005 Mar 23;24(6):1301
Abstract
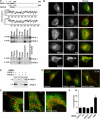
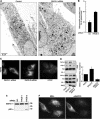
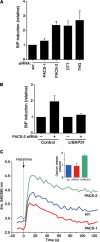
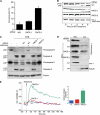
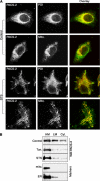
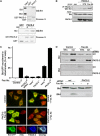
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria form contacts that support communication between these two organelles, including synthesis and transfer of lipids, and the exchange of calcium, which regulates ER chaperones, mitochondrial ATP production, and apoptosis. Despite the fundamental roles for ER-mitochondria contacts, little is known about the molecules that regulate them. Here we report the identification of a multifunctional sorting protein, PACS-2, that integrates ER-mitochondria communication, ER homeostasis, and apoptosis. PACS-2 controls the apposition of mitochondria with the ER, as depletion of PACS-2 causes BAP31-dependent mitochondria fragmentation and uncoupling from the ER. PACS-2 also controls formation of ER lipid-synthesizing centers found on mitochondria-associated membranes and ER homeostasis. However, in response to apoptotic inducers, PACS-2 translocates Bid to mitochondria, which initiates a sequence of events including the formation of mitochondrial truncated Bid, the release of cytochrome c, and the activation of caspase-3, thereby causing cell death. Together, our results identify PACS-2 as a novel sorting protein that links the ER-mitochondria axis to ER homeostasis and the control of cell fate, and provide new insights into Bid action.
Figures
References
-
- Arvidson B, Seeds J, Webb M, Finlay L, Barklis E (2003) Analysis of the retrovirus capsid interdomain linker region. Virology 308: 166–177 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ (2002) The endoplasmic reticulum: a multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium 32: 235–249 - PubMed
-
- Blagoveshchenskaya AD, Thomas L, Feliciangeli SF, Hung CH, Thomas G (2002) HIV-1 Nef downregulates MHC-I by a PACS-1- and PI3K-regulated ARF6 endocytic pathway. Cell 111: 853–866 - PubMed
-
- Boatright KM, Salvesen GS (2003) Mechanisms of caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 725–731 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

