Central role of Ifh1p-Fhl1p interaction in the synthesis of yeast ribosomal proteins
- PMID: 15692568
- PMCID: PMC548658
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600553
Central role of Ifh1p-Fhl1p interaction in the synthesis of yeast ribosomal proteins
Abstract
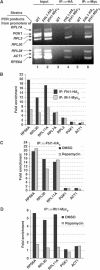
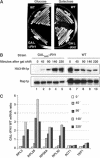
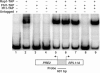
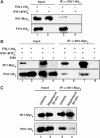
The 138 genes encoding the 79 ribosomal proteins (RPs) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae form the tightest cluster of coordinately regulated genes in nearly all transcriptome experiments. The basis for this observation remains unknown. We now provide evidence that two factors, Fhl1p and Ifh1p, are key players in the transcription of RP genes. Both are found at transcribing RP genes in vivo. Ifh1p, but not Fhl1p, leaves the RP genes when transcription is repressed. The occupancy of the RP genes by Ifh1p depends on its interaction with the phospho-peptide recognizing forkhead-associated domain of Fhl1p. Disruption of this interaction is severely deleterious to ribosome synthesis and cell growth. Loss of functional Fhl1p leads to cells that have only 20% the normal amount of RNA and that synthesize ribosomes at only 5-10% the normal rate. Homeostatic mechanisms within the cell respond by reducing the transcription of rRNA to match the output of RPs, and by reducing the global transcription of mRNA to match the capacity of the translational apparatus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The yeast CPC2/ASC1 gene is regulated by the transcription factors Fhl1p and Ifh1p.Curr Genet. 2006 Apr;49(4):218-28. doi: 10.1007/s00294-005-0049-7. Epub 2006 Jan 10. Curr Genet. 2006. PMID: 16402205
-
The transcription factor Ifh1 is a key regulator of yeast ribosomal protein genes.Nature. 2004 Dec 23;432(7020):1054-8. doi: 10.1038/nature03175. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15616568
-
Growth-regulated recruitment of the essential yeast ribosomal protein gene activator Ifh1.Nature. 2004 Dec 23;432(7020):1058-61. doi: 10.1038/nature03200. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15616569
-
DNA protein interactions at the rRNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Ital J Biochem. 2007 Jun;56(2):81-90. Ital J Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17722648 Review.
-
Synthesis of ribosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):256-71. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.256-271.1989. Microbiol Rev. 1989. PMID: 2666845 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide base editor screen identifies regulators of protein abundance in yeast.Elife. 2022 Nov 3;11:e79525. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79525. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36326816 Free PMC article.
-
Fpr1, a primary target of rapamycin, functions as a transcription factor for ribosomal protein genes cooperatively with Hmo1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jun 30;16(6):e1008865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008865. eCollection 2020 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32603360 Free PMC article.
-
An HMG protein, Hmo1, associates with promoters of many ribosomal protein genes and throughout the rRNA gene locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 May;26(9):3672-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.9.3672-3679.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16612005 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomal degradation of Sfp1 contributes to the repression of ribosome biogenesis during starvation and is mediated by the proteasome activator Blm10.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Mar 1;22(5):528-40. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-04-0352. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21209318 Free PMC article.
-
Gcn4p-mediated transcriptional repression of ribosomal protein genes under amino-acid starvation.EMBO J. 2011 Mar 2;30(5):859-72. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.332. Epub 2010 Dec 24. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21183953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angus-Hill ML, Schlichter A, Roberts D, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Cairns BR (2001) A Rsc3/Rsc30 zinc cluster dimer reveals novel roles for the chromatin remodeler RSC in gene expression and cell cycle control. Mol Cell 7: 741–751 - PubMed
-
- Beer MA, Tavazoie S (2004) Predicting gene expression from sequence. Cell 117: 185–198 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

