BCL1 lymphoma protection induced by idiotype DNA vaccination is entirely dependent on anti-idiotypic antibodies
- PMID: 15692846
- PMCID: PMC11033016
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-004-0579-8
BCL1 lymphoma protection induced by idiotype DNA vaccination is entirely dependent on anti-idiotypic antibodies
Abstract
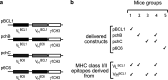
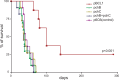
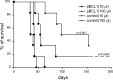
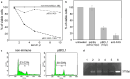
DNA vaccination with the idiotype (Id) of tumour B-cell membrane immunoglobulins (Ig) is a validated strategy to induce tumour protection to several mouse lymphomas. The relative contribution of anti-Id antibodies and T lymphocytes to tumour rejection is still debated. Previous studies in the BCL1 lymphoma model showed that scFv DNA immunisation induces a polyclonal antibody response restricted to conformational epitopes formed by the parental V(L)/V(H) association. We implemented a system based on this specificity to investigate the mechanism of BCL1 lymphoma protection induced by DNA immunisation. Antibody response and survival of mice immunised with the tumour Id scFv were compared with those of mice immunised simultaneously with two chimeric scFvs, containing either the tumour-derived V(L) or V(H) paired to an irrelevant V(H) or V(L) domain, respectively. Animals vaccinated with one or both chimeric constructs were not protected, despite the exposure to all putative tumour Id-derived MHC class I and class II T-cell epitopes. In addition, conformational antibodies induced by DNA vaccination caused tumour cells apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in vitro and transferred protection in vivo. Therefore, lymphoma rejection appears to be completely dependent on the induction of anti-Id antibodies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-idiotypic antibodies induced by genetic immunisation are directed exclusively against combined V(L)/V(H) determinants.Gene Ther. 2001 Oct;8(20):1555-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301546. Gene Ther. 2001. PMID: 11704816
-
Immunization with a recombinant adenovirus encoding a lymphoma idiotype: induction of tumor-protective immunity and identification of an idiotype-specific T cell epitope.J Immunol. 2002 Apr 15;168(8):3983-91. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.8.3983. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11937555
-
A stable single-chain variable fragment expressing transfectoma demonstrates induction of idiotype-specific cytotoxic T-cells during early growth stages of a murine B-lymphoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2001 Oct;50(8):437-44. doi: 10.1007/s002620100208. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2001. PMID: 11726138 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic approach to idiotypic vaccination for B cell lymphoma.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Nov 27;772:212-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb44747.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 8546396 Review.
-
Idiotypic vaccination for B-cell malignancies as a model for therapeutic cancer vaccines: from prototype protein to second generation vaccines.Haematologica. 2002 Sep;87(9):989-1001. Haematologica. 2002. PMID: 12217812 Review.
Cited by
-
Dengue E Protein Domain III-Based DNA Immunisation Induces Strong Antibody Responses to All Four Viral Serotypes.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 Jul 28;9(7):e0003947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003947. eCollection 2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 26218926 Free PMC article.
-
Developing idiotype vaccines for lymphoma: from preclinical studies to phase III clinical trials.Br J Haematol. 2008 Jun;142(2):179-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07143.x. Epub 2008 Apr 13. Br J Haematol. 2008. PMID: 18422783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Idiotypes as immunogens: facing the challenge of inducing strong therapeutic immune responses against the variable region of immunoglobulins.Front Oncol. 2012 Nov 9;2:159. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00159. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23162790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong AC, Dermime S, Allinson CG, Bhattacharyya T, Mulryan K, Gonzalez KR, Stern PL, Hawkins RE. Immunization with a recombinant adenovirus encoding a lymphoma idiotype: induction of tumor-protective immunity and identification of an idiotype-specific T cell epitope. J Immunol. 2002;168:3983. - PubMed
-
- Benvenuti F, Cesco-Gaspere M, Burrone OR. Anti-idiotypic DNA vaccines for B-cell lymphoma therapy. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

