Antibody-targeted chemotherapy of B-cell lymphoma using calicheamicin conjugated to murine or humanized antibody against CD22
- PMID: 15693135
- PMCID: PMC11033002
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-004-0572-2
Antibody-targeted chemotherapy of B-cell lymphoma using calicheamicin conjugated to murine or humanized antibody against CD22
Abstract
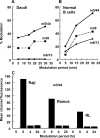
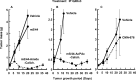
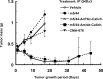
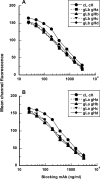
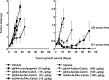
Antibody-targeted chemotherapy with immunoconjugates of calicheamicin is a clinically validated strategy in cancer therapy. This study describes the selection of a murine anti-CD22 mAb, m5/44, as a targeting agent, its conjugation to a derivative of calicheamicin (CalichDM) via either acid-labile or acid-stable linkers, the antitumor activity of CalichDM conjugated to m5/44, and its subsequent humanization by CDR grafting. Murine IgG1 mAb m5/44 was selected based on its subnanomolar affinity for CD22 and ability to be internalized into B cells. CalichDM conjugated to m5/44 caused potent growth inhibition of CD22+ human B-cell lymphomas (BCLs) in vitro. The conjugate of m5/44 with an acid-labile linker was more potent than an acid-stable conjugate, a nonbinding conjugate with a similar acid-labile linker, or unconjugated CalichDMH in inhibiting BCL growth. CalichDM conjugated to m5/44 caused regression of established BCL xenografts in nude mice. In contrast, both unconjugated m5/44 and a nonbinding conjugate were ineffective against these xenografts. Based on the potent antitumor activity of m5/44-CalichDM conjugates, m5/44 was humanized by CDR grafting to create g5/44, an IgG4 anti-CD22 antibody. Both m5/44 and g5/44 bound CD22 with subnanomolar affinity. Competitive blocking with previously characterized murine anti-CD22 mAbs suggested that g5/44 recognizes epitope A located within the first N-terminal Ig-like domain of human CD22. Antitumor efficacy of CalichDM conjugated to g5/44 against BCL xenografts was more potent than its murine counterpart. Based on these results, a calicheamicin conjugate of g5/44, CMC-544, was selected for further development as a targeted chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of B-cell malignancies.
Figures
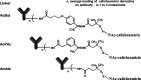


Similar articles
-
Antibody-targeted chemotherapy with CMC-544: a CD22-targeted immunoconjugate of calicheamicin for the treatment of B-lymphoid malignancies.Blood. 2004 Mar 1;103(5):1807-14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-07-2466. Epub 2003 Nov 13. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14615373
-
Antibody-targeted chemotherapy with immunoconjugates of calicheamicin.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003 Aug;3(4):386-90. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4892(03)00083-3. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12901947 Review.
-
Potent and specific antitumor efficacy of CMC-544, a CD22-targeted immunoconjugate of calicheamicin, against systemically disseminated B-cell lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Dec 15;10(24):8620-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1134. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15623646
-
Anti-CD22 ligand-blocking antibody HB22.7 has independent lymphomacidal properties and augments the efficacy of 90Y-DOTA-peptide-Lym-1 in lymphoma xenografts.Blood. 2003 May 1;101(9):3641-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-08-2629. Epub 2003 Jan 2. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12511412
-
Tumour-targeted chemotherapy with immunoconjugates of calicheamicin.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004 Sep;4(9):1445-52. doi: 10.1517/14712598.4.9.1445. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15335312 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibody-Drug Conjugates for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies: A Comprehensive Review.Target Oncol. 2018 Jun;13(3):287-308. doi: 10.1007/s11523-018-0558-1. Target Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29556925 Review.
-
Novel antibody-based proteins for cancer immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Aug 19;3(3):3370-93. doi: 10.3390/cancers3033370. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24212958 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural insights of the early glycosylation steps in calicheamicin biosynthesis.Chem Biol. 2008 Aug 25;15(8):842-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.06.011. Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 18721755 Free PMC article.
-
Specific targeting to B cells by lipid-based nanoparticles conjugated with a novel CD22-ScFv.Exp Mol Pathol. 2010 Apr;88(2):238-49. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.01.006. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Exp Mol Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20122924 Free PMC article.
-
DNTT-mediated DNA damage response drives inotuzumab ozogamicin resistance in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 2025 Mar 13;145(11):1182-1194. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024026085. Blood. 2025. PMID: 39791601
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

