Interventions to prevent chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations
- PMID: 15693642
- PMCID: PMC7185512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2004.10.021
Interventions to prevent chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations
Abstract
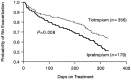
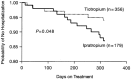
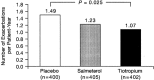
Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have a profound effect on the patient's health status and decline in lung function; they also impose a significant burden on healthcare resource utilization. Prevention and treatment of exacerbations is listed by the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) as among the major objectives of COPD management, and it is therefore an important outcome measure when studying any new agent. This article discusses pharmacologic therapy and other measures for preventing exacerbations and hospitalizations due to exacerbations of COPD.
Figures
References
-
- Anthonisen N.R., Manfreda J., Warren C.P., Hershfield E.S., Harding G.K., Nelson N.A. Antibiotic therapy in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:196–204. - PubMed
-
- Seemungal T.A., Donaldson G.C., Bhowmik A., Jeffries D.J., Wedzicha J.A. Time course and recovery of exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:1608–1613. - PubMed
-
- Monso E., Ruiz J., Rosell A. Bacterial infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a study of stable and exacerbated outpatients using the protected specimen brush. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152(Pt 1):1316–1320. - PubMed
-
- Eller J., Ede A., Schaberg T., Niederman M.S., Mauch H., Lode H. Infective exacerbations of chronic bronchitis: relation between bacteriologic etiology and lung function. Chest. 1998;113:1542–1548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

