Influence of language and ancestry on genetic structure of contiguous populations: a microsatellite based study on populations of Orissa
- PMID: 15694006
- PMCID: PMC549189
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-4
Influence of language and ancestry on genetic structure of contiguous populations: a microsatellite based study on populations of Orissa
Abstract
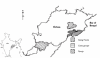
Background: We have examined genetic diversity at fifteen autosomal microsatellite loci in seven predominant populations of Orissa to decipher whether populations inhabiting the same geographic region can be differentiated on the basis of language or ancestry. The studied populations have diverse historical accounts of their origin, belong to two major ethnic groups and different linguistic families. Caucasoid caste populations are speakers of Indo-European language and comprise Brahmins, Khandayat, Karan and Gope, while the three Australoid tribal populations include two Austric speakers: Juang and Saora and a Dravidian speaking population, Paroja. These divergent groups provide a varied substratum for understanding variation of genetic patterns in a geographical area resulting from differential admixture between migrants groups and aboriginals, and the influence of this admixture on population stratification.
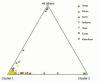
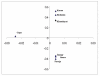
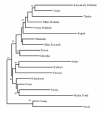
Results: The allele distribution pattern showed uniformity in the studied groups with approximately 81% genetic variability within populations. The coefficient of gene differentiation was found to be significantly higher in tribes (0.014) than caste groups (0.004). Genetic variance between the groups was 0.34% in both ethnic and linguistic clusters and statistically significant only in the ethnic apportionment. Although the populations were genetically close (FST = 0.010), the contemporary caste and tribal groups formed distinct clusters in both Principal-Component plot and Neighbor-Joining tree. In the phylogenetic tree, the Orissa Brahmins showed close affinity to populations of North India, while Khandayat and Gope clustered with the tribal groups, suggesting a possibility of their origin from indigenous people.
Conclusions: The extent of genetic differentiation in the contemporary caste and tribal groups of Orissa is highly significant and constitutes two distinct genetic clusters. Based on our observations, we suggest that since genetic distances and coefficient of gene differentiation were fairly small, the studied populations are indeed genetically similar and that the genetic structure of populations in a geographical region is primarily influenced by their ancestry and not by socio-cultural hierarchy or language. The scenario of genetic structure, however, might be different for other regions of the subcontinent where populations have more similar ethnic and linguistic backgrounds and there might be variations in the patterns of genomic and socio-cultural affinities in different geographical regions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A microsatellite study to disentangle the ambiguity of linguistic, geographic, ethnic and genetic influences on tribes of India to get a better clarity of the antiquity and peopling of South Asia.Am J Phys Anthropol. 2009 Aug;139(4):533-46. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.21018. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2009. PMID: 19278019
-
Genomic congruence of Indo-European speaking tribes of western India with Dravidian-speaking populations of southern India: A study of 20 autosomal DNA markers.Ann Hum Biol. 2011 Sep;38(5):583-91. doi: 10.3109/03014460.2011.577455. Epub 2011 May 11. Ann Hum Biol. 2011. PMID: 21561300
-
Genetic structure of four socio-culturally diversified caste populations of southwest India and their affinity with related Indian and global groups.BMC Genet. 2004 Aug 19;5:23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-5-23. BMC Genet. 2004. PMID: 15317657 Free PMC article.
-
Population structure of the Chenchu and other south Indian tribal groups: relationships between genetic, anthropometric, dermatoglyphic, geographic, and linguistic distances.Hum Biol. 1994 Oct;66(5):865-84. Hum Biol. 1994. PMID: 8001914 Review.
-
Genetic variation in India.Hum Biol. 1996 Oct;68(5):607-28. Hum Biol. 1996. PMID: 8908794 Review.
Cited by
-
Low levels of genetic divergence across geographically and linguistically diverse populations from India.PLoS Genet. 2006 Dec;2(12):e215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020215. PLoS Genet. 2006. PMID: 17194221 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic relationships of ethnic minorities in Southwest China revealed by microsatellite markers.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 29;5(3):e9895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009895. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20360948 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic structure of Indian populations based on fifteen autosomal microsatellite loci.BMC Genet. 2006 May 17;7:28. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-7-28. BMC Genet. 2006. PMID: 16707019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cavalli-Sforza LL, Menozzi P, Piazza A. The history and geography of Human genes. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1994.
-
- Gadgil M, Joshi NV, Shambu Prasad UV, Manoharan S, Patil S. The Indian Human Heritage. Universities Press, Hyderabad, India; 1997. Peopling of India; pp. 100–129.
-
- Papiha SS. Genetic variation in India. Hum Biol. 1996;68:607–628. - PubMed
-
- Reddy BM, Sun G, Rodriguez-Luis J, Crawford MH, Hemam NS, Deka R. Genomic diversity at thirteen short tandem repeat loci in a substructured caste population, Golla, of southern Andhra Pradesh, India. Hum Biol. 2001;73:175–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

