Cross-host evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in palm civet and human
- PMID: 15695582
- PMCID: PMC548959
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409608102
Cross-host evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in palm civet and human
Abstract
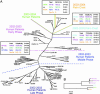
The genomic sequences of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses from human and palm civet of the 2003/2004 outbreak in the city of Guangzhou, China, were nearly identical. Phylogenetic analysis suggested an independent viral invasion from animal to human in this new episode. Combining all existing data but excluding singletons, we identified 202 single-nucleotide variations. Among them, 17 are polymorphic in palm civets only. The ratio of nonsynonymous/synonymous nucleotide substitution in palm civets collected 1 yr apart from different geographic locations is very high, suggesting a rapid evolving process of viral proteins in civet as well, much like their adaptation in the human host in the early 2002-2003 epidemic. Major genetic variations in some critical genes, particularly the Spike gene, seemed essential for the transition from animal-to-human transmission to human-to-human transmission, which eventually caused the first severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak of 2002/2003.
Figures
References
-
- Ksiazek, T. G., Erdman, D., Goldsmith, C. S., Zaki, S. R., Peret, T., Emery, S., Tong, S., Urbani, C., Comer, J. A., Lim, W., et al. (2003) N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1953-1966. - PubMed
-
- Drosten, C., Gunther, S., Preiser, W., van der Werf, S., Brodt, H. R., Becker, S., Rabenau, H., Panning, M., Kolesnikova, L., Fouchier, R. A., et al. (2003) N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1967-1976. - PubMed
-
- Rota, P. A., Oberste, M. S., Monroe, S. S., Nix, W. A., Campagnoli, R., Icenogle, J. P., Penaranda, S., Bankamp, B., Maher, K., Chen, M. H., et al. (2003) Science 300, 1394-1399. - PubMed
-
- Marra, M. A., Jones, S. J., Astell, C. R., Holt, R. A., Brooks-Wilson, A., Butterfield, Y. S., Khattra, J., Asano, J. K., Barber, S. A., Chan, S. Y., et al. (2003) Science 300, 1399-1404. - PubMed
-
- Guan. Y., Zheng, B. J., He, Y. Q., Liu, X. L., Zhuang, Z. X., Cheung, C. L., Luo, S. W., Li, P. H., Zhang, L. J., Guan, Y. J., et al. (2003) Science 302, 276-278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

