Complexes in ternary cholesterol-phospholipid mixtures
- PMID: 15695625
- PMCID: PMC1305398
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.058834
Complexes in ternary cholesterol-phospholipid mixtures
Abstract
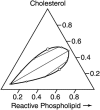
Recent work by Veatch and Keller has described micron-scale liquid-liquid immiscibility in giant unilamellar vesicles composed of ternary mixtures of cholesterol, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), and dioleoylphosphatidylcholine (DOPC). Significantly, they do not observe micron-scale immiscibility in any of the three corresponding binary mixtures under the same conditions. It is shown here that this unexpected result can be accounted for by the formation of a complex between cholesterol and DPPC. The complex is miscible with DPPC and cholesterol, and immiscible with DOPC. A simple, idealized thermodynamic treatment of this model leads to theoretical ternary phase diagrams that are similar to the experimental diagram reported by Veatch and Keller. The model also accounts for significant qualitative features of the deuterium NMR spectra of these mixtures in bilayers.
Figures
References
-
- McConnell, H., and A. Radhakrishnan. 2003. Condensed complexes of cholesterol and phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1610:159–173. - PubMed
-
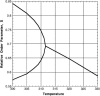
- Vist, M. R., and J. H. Davis. 1990. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 29:451–464. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

