Duplex PCR to differentiate between Mycoplasma synoviae and Mycoplasma gallisepticum on the basis of conserved species-specific sequences of their hemagglutinin genes
- PMID: 15695715
- PMCID: PMC548031
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.948-950.2005
Duplex PCR to differentiate between Mycoplasma synoviae and Mycoplasma gallisepticum on the basis of conserved species-specific sequences of their hemagglutinin genes
Abstract
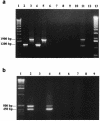
We developed a duplex PCR assay targeting the hemagglutinin multigene families, vlhA and pMGA, of Mycoplasma synoviae and Mycoplasma gallisepticum, respectively. The assay proved to be specific and sensitive enough to justify its use for the simultaneous detection of the two major avian mycoplasma species from field isolates.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a duplex real-time TaqMan PCR assay with an internal control for the detection of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma synoviae in clinical samples from commercial and backyard poultry.Avian Pathol. 2010 Apr;39(2):99-109. doi: 10.1080/03079451003604621. Avian Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20390544
-
Rapid and specific detection of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma synoviae infection in poultry using single and duplex PCR assays.J Microbiol Methods. 2022 Jan;192:106365. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106365. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Microbiol Methods. 2022. PMID: 34774671
-
Specific detection and typing of Mycoplasma synoviae strains in poultry with PCR and DNA sequence analysis targeting the hemagglutinin encoding gene vlhA.Avian Dis. 2004 Sep;48(3):606-16. doi: 10.1637/7156-011504R. Avian Dis. 2004. PMID: 15529983
-
Haemagglutinins of pathogenic avian mycoplasmas.Avian Pathol. 2002 Dec;31(6):535-47. doi: 10.1080/0307945021000024526. Avian Pathol. 2002. PMID: 12593736 Review.
-
Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma synoviae in commercial poultry: current control strategies and future challenges.Avian Pathol. 2025 Apr;54(2):168-174. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2024.2419037. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Avian Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39471302 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Mycoplasma gallisepticum, Mycoplama synoviae, and infectious bronchitis virus in poultry in Myanmar.BMC Vet Res. 2019 Jul 25;15(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-2018-2. BMC Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 31345206 Free PMC article.
-
First molecular investigation to detect avian Mycoplasma species in clinical samples from laying-hen farms in Tunisia.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Oct 10;20(1):459. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04311-5. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39390571 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid serodiagnosis with the use of surface plasmon resonance imaging for the detection of antibodies against major surface protein A of Mycoplasma synoviae in chickens.Can J Vet Res. 2010 Jan;74(1):71-4. Can J Vet Res. 2010. PMID: 20357963 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and differentiation of avian mycoplasmas by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy based on a silver nanorod array.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Mar;78(6):1930-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07419-11. Epub 2011 Dec 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22210215 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of Mycoplasma synoviae from seroprevalent commercial breeder farms at Chittagong district, Bangladesh.Vet World. 2016 Oct;9(10):1063-1069. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2016.1063-1069. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Vet World. 2016. PMID: 27847414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben Abdelmoumen, B., and R. S. Roy. 1995. Antigenic relatedness between seven avian mycoplasma species as revealed by Western blot analysis. Avian Dis. 39:250-262. - PubMed
-
- Ben Abdelmoumen, B., and R. S. Roy. 1995. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of avian mycoplasmas in culture. Avian Dis. 39:85-93. - PubMed
-
- Ben Abdelmoumen, B., R. S. Roy, and R. Brousseau. 1999. Cloning of Mycoplasma synoviae genes encoding specific antigens and their use as species-specific DNA probes. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 11:162-169. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury, J. M., and F. T. W. Jordan. 1971. The adsorption of gamma globulins to Mycoplasma gallisepticum and the possible role in nonspecific serological reactions. Vet. Rec. 89:318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

