Nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi presenting as a primary psoas abscess: case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 15695728
- PMCID: PMC548044
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.996-998.2005
Nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi presenting as a primary psoas abscess: case report and review of the literature
Abstract
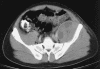
We report an unusual case of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi presenting as a primary psoas abscess. The isolate tested susceptible to ciprofloxacin but resistant to nalidixic acid in vitro, a pattern associated with fluoroquinolone therapeutic failures. We review the literature for serovar Typhi psoas abscess in the absence of bacteremia and discuss the importance of identifying isolates with reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suboptimal clinical response to ciprofloxacin in patients with enteric fever due to Salmonella spp. with reduced fluoroquinolone susceptibility: a case series.BMC Infect Dis. 2004 Sep 20;4:36. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-4-36. BMC Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15380025 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi resistant to ciprofloxacin in India.J Med Microbiol. 2007 Jan;56(Pt 1):136-137. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46763-0. J Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17172529 No abstract available.
-
Reevaluating fluoroquinolone breakpoints for Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi and for non-Typhi salmonellae.Clin Infect Dis. 2003 Jul 1;37(1):75-81. doi: 10.1086/375602. Epub 2003 Jun 20. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12830411
-
In vitro efficacy of the combination of ciprofloxacin and cefotaxime against nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010 Aug;36(2):155-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.03.022. Epub 2010 May 15. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010. PMID: 20478696
-
A case report and review of the literature: ciprofloxacin resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi in India.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008 Aug 30;2(4):324-7. doi: 10.3855/jidc.229. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008. PMID: 19741296 Review.
Cited by
-
High prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among Shigella isolates in the United States tested by the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System from 1999 to 2002.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jan;50(1):49-54. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.1.49-54.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16377666 Free PMC article.
-
Typhoid fever as a cause of opportunistic infection: case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2006 Feb 27;6:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-38. BMC Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16504150 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Anterior Thoracic Wall Abscess with Osteomyelitis by Salmonella paratyphi A : Case Report.J Lab Physicians. 2023 Jul 10;15(4):613-615. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1768949. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Lab Physicians. 2023. PMID: 37780877 Free PMC article.
-
Fever of unknown origin attributable to haematocolpos infected with Salmonella enterica Serotypetyphi resistant to nalidixic acid: a case report.J Health Popul Nutr. 2013 Sep;31(3):403-4. doi: 10.3329/jhpn.v31i3.16833. J Health Popul Nutr. 2013. PMID: 24288955 Free PMC article.
-
Relapse of typhoid fever following delayed response to meropenem: A case report and review of previously published cases indicating limited clinical efficacy of meropenem for the treatment of typhoid fever.Ger Med Sci. 2019 Jan 7;17:Doc01. doi: 10.3205/000267. eCollection 2019. Ger Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30837820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baccaro, F. G. 1999. Primary psoas abscess due to Salmonella typhi. Med. Gen. Med. 10:E16. - PubMed
-
- Ciraj, A. M., D. Reetika, G. K. Bhat, C. G. Pai, and P. G. Shivananda. 2002. Hepatic abscess caused by Salmonella typhi. Trop. Gastroenterol. 23:181-182. - PubMed
-
- Crump, J. A., T. J. Barrett, J. T. Nelson, and F. J. Angulo. 2003. Reevaluating fluoroquinolone breakpoints for Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi and for non-Typhi salmonellae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 37:75-81. - PubMed
-
- Hanel, R. A., J. C. Araujo, A. Antoniuk, L. F. da Silva Ditzel, L. T. Flenik Martins, and M. N. Linhares. 2000. Multiple brain abscesses caused by Salmonella typhi: case report. Surg. Neurol. 53:86-90. - PubMed
-
- Heyd, J., R. Meallem, Y. Schlesinger, B. Rudensky, I. Hadas-Halpern, A. M. Yinnon, and D. Raveh. 2003. Clinical characteristics of patients with psoas abscess due to non-typhi Salmonella. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 22:770-773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical