Identification of pathway-selective estrogen receptor ligands that inhibit NF-kappaB transcriptional activity
- PMID: 15699342
- PMCID: PMC548967
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0405841102
Identification of pathway-selective estrogen receptor ligands that inhibit NF-kappaB transcriptional activity
Abstract
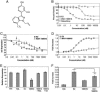
Inflammation is now recognized as a key component in a number of diseases such as atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. The transcription factor NF-kappaB has been shown to be involved in both the early and late stages of the inflammatory-proliferative process. In this report, we describe the identification of the pathway-selective estrogen receptor (ER) ligand, WAY-169916, that inhibits NF-kappaB transcriptional activity but is devoid of conventional estrogenic activity. This pathway-selective ligand does not promote the classic actions of estrogens such as stimulation of uterine proliferation or ER-mediated gene expression, but is a potent antiinflammatory agent, as demonstrated in the HLA-B27 transgenic rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. Our results indicate the potential utility of pathway-selective ER ligands such as WAY-169916 in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures
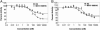

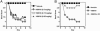
References
-
- Lentsch, A. B. & Ward, P. A. (2000) J. Pathol. 190, 343-348. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, P. J. & Karin, M. (1997) N. Engl. J. Med. 336, 1066-1071. - PubMed
-
- Pahl, H. L. (1999) Oncogene 18, 6853-6866. - PubMed
-
- Evans, M. J., Harris, H. A., Miller, C. P., Karathanasis, S. K. & Adelman, S. J. (2002) Endocrinology 143, 3785-3795. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

