The role of substance P in microvascular responses in murine joint inflammation
- PMID: 15700029
- PMCID: PMC1576088
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706131
The role of substance P in microvascular responses in murine joint inflammation
Abstract
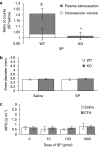
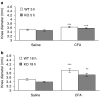
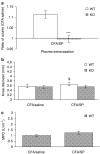
1. Rheumatoid arthritis is a serious, inflammatory disease of the distal joints that has a possible neurogenic component underlying its pathology. 2. Substance P (SP), an endogenous neuropeptide that acts upon the neurokinin 1 (NK(1)) receptor, is released from sensory nerves and is involved in neurogenic inflammation. 3. In this study, we have developed novel techniques to determine the contribution of SP to microvascular responses in a model of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis in NK(1) knockout mice. 4. Detailed analysis in normal mice revealed that CFA (20 microg i.art.)-induced plasma extravasation was raised from 18 to 72 h, when compared with intravascular volume. By comparison, knee swelling was sustained for 3 weeks. Neutrophil accumulation mirrored plasma extravasation. SP (10 pmol i.art.) caused significant acute plasma extravasation, but not other parameters, in wild type (WT), but not NK(1) knockout mice. CFA (10 microg i.art.) induced a significantly decreased intravascular volume, presumably due to decreased blood flow, at early time points (5 and 7 h) in WT but not NK(1) knockouts. Otherwise, similar responses in WT and NK(1) knockout mice were observed. However, injection of SP into CFA-pretreated joints caused a significant enhancement of plasma extravasation and knee swelling in the WT but not NK(1) knockouts. 5. In conclusion, the present study has used novel techniques in WT and NK(1) knockout mice to show that SP can modulate vascular tone and permeability in the inflamed joint via activation of the NK(1) receptor and that SP-induced responses are more pronounced where pre-existing inflammation is present.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in the vascular and hyperalgesic components of joint inflammation.Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Oct;52(10):3248-56. doi: 10.1002/art.21297. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 16200599
-
Involvement of substance P in the antinociceptive effect of botulinum toxin type A: Evidence from knockout mice.Neuroscience. 2017 Sep 1;358:137-145. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.06.040. Epub 2017 Jul 1. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28673722
-
Environmental cold exposure increases blood flow and affects pain sensitivity in the knee joints of CFA-induced arthritic mice in a TRPA1-dependent manner.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Jan 11;18:7. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0905-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 26754745 Free PMC article.
-
A role for substance P in arthritis?Neurosci Lett. 2004 May 6;361(1-3):176-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.020. Neurosci Lett. 2004. PMID: 15135922 Review.
-
Substance P and its Inhibition in Ocular Inflammation.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(11):1265-74. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666151019100216. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26477461 Review.
Cited by
-
Substance P participates in immune-mediated hepatic injury induced by concanavalin A in mice and stimulates cytokine synthesis in Kupffer cells.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Aug;6(2):459-464. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1152. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 24137208 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of functional ryanodine receptors in rat mesenteric collecting lymphatic vessels.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Sep 1;317(3):H561-H574. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00564.2018. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31274355 Free PMC article.
-
Hemokinin-1 as a Mediator of Arthritis-Related Pain via Direct Activation of Primary Sensory Neurons.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 13;11:594479. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.594479. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33519457 Free PMC article.
-
Calotropis procera latex extract affords protection against inflammation and oxidative stress in Freund's complete adjuvant-induced monoarthritis in rats.Mediators Inflamm. 2007;2007:47523. doi: 10.1155/2007/47523. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Mediators Inflamm. 2007. PMID: 17497032 Free PMC article.
-
Differential inflammation-mediated function of prokineticin 2 in the synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with osteoarthritis.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 15;11(1):18399. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97809-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34526577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AHLQVIST J. Swelling of synovial joints – an anatomical, physiological and energy metabolical approach. Pathophysiology. 2000;7:1–19. - PubMed
-
- BÖCKMANN S., SEEP J., JONES L. Delay of neutrophil apoptosis by the neuropeptide substance P: involvement of caspase cascade. Peptides. 2001;22:661–670. - PubMed
-
- BULLING D.G., KELLY D., BOND S., MCQUEEN D.S., SECKL J.R. Adjuvant-induced joint inflammation causes a very rapid transcription of beta-preprotachykinin and alpha-CGRP genes in innervating sensory ganglia. J. Neurochem. 2001;77:372–382. - PubMed
-
- CAO T., GERARD N.P., BRAIN S.D. Use of NK1 knockout mice to analyze substance P-induced edema formation. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;277:R476–R481. - PubMed
-
- CAO T., PINTER E., AL-RASHED S., GERARD N., HOULT R., BRAIN S.D. Neurokinin-1 receptor agonists are involved in mediating neutrophil accumulation in the inflamed, but not normal, cutaneous microvasculature: an in vivo study using neurokinin-1 receptor knockout mice. J. Immunol. 2000;164:5424–5429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

