Early endostatin treatment inhibits metastatic seeding of murine colorectal cancer cells in the liver and their adhesion to endothelial cells
- PMID: 15700042
- PMCID: PMC2361873
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602385
Early endostatin treatment inhibits metastatic seeding of murine colorectal cancer cells in the liver and their adhesion to endothelial cells
Abstract
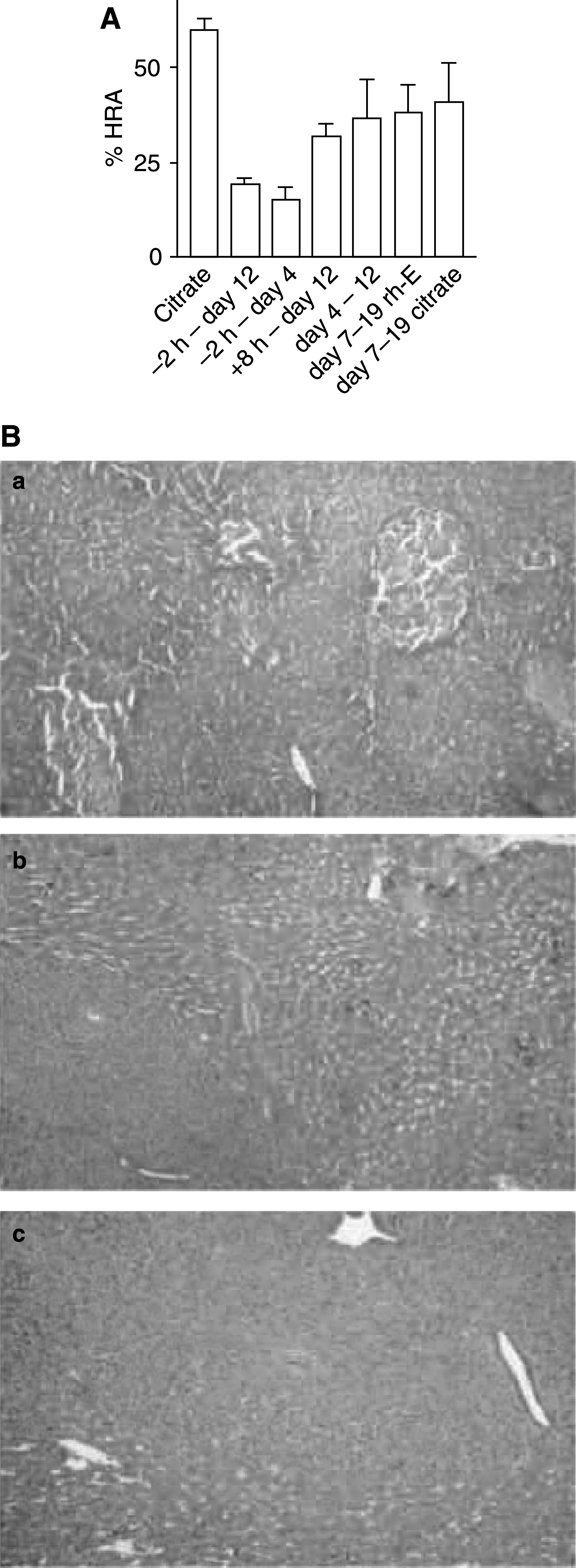
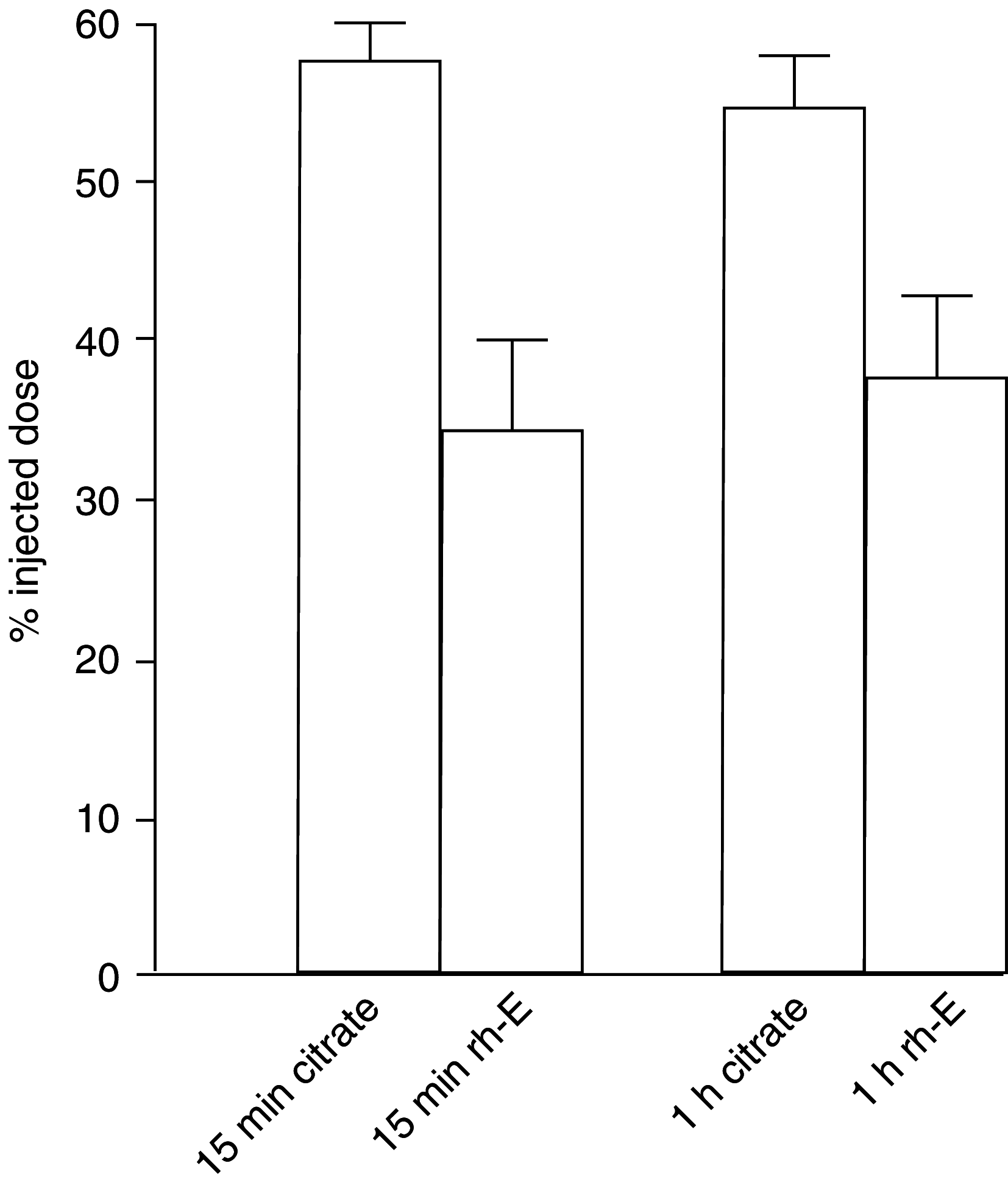
Endostatin, a carboxy-terminal fragment of collagen XVIII, potently inhibits angiogenesis and tumour growth, presumably through induction of apoptosis in endothelial cells and/or inhibition of their migration. Here we have tested how the timing of recombinant human endostatin (rh-E) administration affects its antitumour activity in a liver metastasis model of mouse C26 colorectal carcinoma cells. The effects of rh-E treatment on hepatic tumour load and on early tumour cell seeding were evaluated. Recombinant human endostatin was most effective in reducing intrahepatic tumour growth when administered prior to tumour cell inoculation. Analysis of early tumour cell seeding by using [(125)I]iododeoxyuridine-labelled C26 cells or by in vivo microscopy showed that rh-E reduced tumour cell seeding in the liver sinusoids. Recombinant human endostatin did not inhibit tumour growth when administered later than 4 days after tumour injection. Pretreatment of human umbilical vein endothelial cells with rh-E in vitro reduced C26 tumour cell adhesion under flow conditions two-fold as assessed by video microscopy and multiphoton laser scanning microscopy. Our results show that rh-E, in addition to antiangiogenic effects, reduces tumour cell adhesion in the liver sinusoids during the very early phases of metastasis formation. These data point towards a previously unknown mode of action of endostatin, that is, its ability to interfere with tumour cell seeding. Such insights may be helpful in the design of trials to improve (surgical) treatment of colorectal carcinoma and liver metastases.
Figures

References
-
- Bergers G, Javaherian K, Lo KM, Folkman J, Hanahan D (1999) Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage carcinogenesis in mice. Science 284: 808–812 - PubMed
-
- Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O'Reilly MS (1997) Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature 390: 404–407 - PubMed
-
- Brandsma D, Reijeveld JC, Taphoorn MJ, de Boer HC, Gebbink MF, Ulfman LH, Zwaginga JJ, Voest EE (2002) Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 is a key adhesion molecule in melanoma cell adhesion to the leptomeninges. Lab Invest 82: 1493–1502 - PubMed
-
- Dixelius J, Cross M, Matsumoto T, Sasaki T, Timpl R, Claesson-Welsh L (2002) Endostatin regulates endothelial cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization. Cancer Res 62: 1944–1947 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

