Recent Hits Acquired by BLAST (ReHAB): a tool to identify new hits in sequence similarity searches
- PMID: 15701178
- PMCID: PMC549547
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-23
Recent Hits Acquired by BLAST (ReHAB): a tool to identify new hits in sequence similarity searches
Abstract
Background: Sequence similarity searching is a powerful tool to help develop hypotheses in the quest to assign functional, structural and evolutionary information to DNA and protein sequences. As sequence databases continue to grow exponentially, it becomes increasingly important to repeat searches at frequent intervals, and similarity searches retrieve larger and larger sets of results. New and potentially significant results may be buried in a long list of previously obtained sequence hits from past searches.
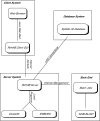
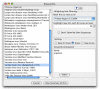
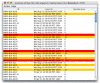
Results: ReHAB (Recent Hits Acquired from BLAST) is a tool for finding new protein hits in repeated PSI-BLAST searches. ReHAB compares results from PSI-BLAST searches performed with two versions of a protein sequence database and highlights hits that are present only in the updated database. Results are presented in an easily comprehended table, or in a BLAST-like report, using colors to highlight the new hits. ReHAB is designed to handle large numbers of query sequences, such as whole genomes or sets of genomes. Advanced computer skills are not needed to use ReHAB; the graphics interface is simple to use and was designed with the bench biologist in mind.
Conclusions: This software greatly simplifies the problem of evaluating the output of large numbers of protein database searches.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

