Critical role of hnRNP A1 in HTLV-1 replication in human transformed T lymphocytes
- PMID: 15703079
- PMCID: PMC551596
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-2-8
Critical role of hnRNP A1 in HTLV-1 replication in human transformed T lymphocytes
Abstract
Background: In this study, we have examined the role of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNP A1) in viral gene expression in T lymphocytes transformed by HTLV-1.
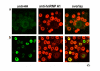
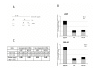
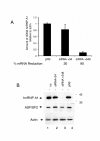
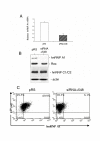
Results: We have previously observed that hnRNP A1 (A1) down-modulates the post transcriptional activity of Rex protein of HTLV-1. Here, we tested whether the ectopic expression of a dominant negative mutant (NLS-A1-HA) defective in shuttling activity or knockdown of the hnRNPA1 gene using RNA interference could inhibit Rex-mediated export of viral mRNAs in HTLV-1 producing C91PL T-cells. We show that the expression of NLS-A1-HA does not modify the export of Rex-dependent viral mRNAs. Conversely, inhibiting A1 expression in C91PL cells by RNA interference provoked an increase in the Rex-dependent export of unspliced and singly spliced mRNAs. Surprisingly, we also observed a significant increase in proviral transcription and an accumulation of unspliced mRNAs, suggesting that the splicing process was affected. Finally, A1 knockdown in C91PL cells increased viral production by these cells. Thus, hnRNP A1 is implicated in the modulation of the level of HTLV-1 gene expression in T cells transformed by this human retrovirus.
Conclusions: These observations provide an insight into a new cellular control of HTLV-1 replication and suggest that hnRNP A1 is likely part of the regulatory mechanisms of the life cycle of this human retrovirus in T cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 interferes with the binding of the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 rex regulatory protein to its response element.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 24;277(21):18744-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109087200. Epub 2002 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11893730
-
Roles of viral and cellular proteins in the expression of alternatively spliced HTLV-1 pX mRNAs.Virology. 2003 Dec 5;317(1):136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2003.09.010. Virology. 2003. PMID: 14675632
-
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNP A1) and hnRNP A2 Inhibit Splicing to Human Papillomavirus 16 Splice Site SA409 through a UAG-Containing Sequence in the E7 Coding Region.J Virol. 2020 Sep 29;94(20):e01509-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01509-20. Print 2020 Sep 29. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32759322 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1 Rex Tunes the Cellular Environment Favorable for Viral Replication.Viruses. 2016 Feb 24;8(3):58. doi: 10.3390/v8030058. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26927155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 in health and neurodegenerative disease: from structural insights to post-transcriptional regulatory roles.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:436-46. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23247072 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping the LINE1 ORF1 protein interactome reveals associated inhibitors of human retrotransposition.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(15):7401-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt512. Epub 2013 Jun 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23749060 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization of the complete genome of a highly divergent simian T-lymphotropic virus (STLV) type 3 from a wild Cercopithecus mona monkey.Retrovirology. 2009 Oct 27;6:97. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-6-97. Retrovirology. 2009. PMID: 19860877 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and characterization of auxiliary proteins encoded by type 3 simian T-cell lymphotropic viruses.J Virol. 2015 Jan 15;89(2):931-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02150-14. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25355890 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 regulates cyclin D1 and c-myc internal ribosome entry site function through Akt signaling.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 22;283(34):23274-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801185200. Epub 2008 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18562319 Free PMC article.
-
Is unphosphorylated Rex, as multifunctional protein of HTLV-1, a fully intrinsically disordered protein? An in silico study.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016 Aug 4;8:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.07.018. eCollection 2016 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016. PMID: 28955936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yoshida M. Multiple targets of HTLV-I for dysregulation of host cells. Seminars in Virology. 1996;7:349–360. doi: 10.1006/smvy.1996.0042. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

