Nuclear translocation of integrin cytoplasmic domain-associated protein 1 stimulates cellular proliferation
- PMID: 15703214
- PMCID: PMC1073667
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0744
Nuclear translocation of integrin cytoplasmic domain-associated protein 1 stimulates cellular proliferation
Abstract
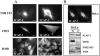
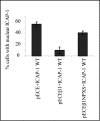
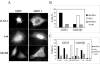
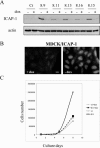
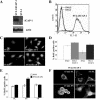
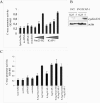
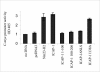
Integrin cytoplasmic domain-associated protein 1 (ICAP-1) has been shown to interact specifically with the beta1 integrin cytoplasmic domain and to control cell spreading on fibronectin. Interestingly, ICAP-1 also is observed in the nucleus, by immunocytochemical staining, and after biochemical cell fractionation, suggesting that it has additional roles that have yet to be determined. We show that the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling capability of ICAP-1 is dependent on a functional nuclear localization signal. In addition, overexpression of beta1 integrin strongly reduced this nuclear localization, suggesting that integrin activity could modulate ICAP-1 shuttling by sequestering it in the cytoplasm. Indeed, the nuclear localization of ICAP-1 is dependent on the stage of cell spreading on fibronectin, and we also show that ICAP-1 expression stimulates cellular proliferation in a fibronectin-dependent manner. This function is dependent on its nuclear localization. Moreover, ICAP-1 is able to activate the c-myc promoter in vitro. Together, these results demonstrate that ICAP-1 shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm in a beta1 integrin-dependent manner. It could act as a messenger that relays information from sites of integrin-dependent cell adhesion to the nucleus for controlling gene expression and cell proliferation.
Figures


References
-
- Barberis, L., Wary, K. K., Fiucci, G., Liu, F., Hirsch, E., Brancaccio, M., Altruda, F., Tarone, G., and Giancotti, F. G. (2000). Distinct roles of the adaptor protein Shc and focal adhesion kinase in integrin signaling to ERK. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 36532-36540. - PubMed
-
- Barone, M. V., and Courtneidge, S. A. (1995). Myc but not Fos rescue of platelet-derived growth factor signalling block caused by kinase-inactive Src. Nature 378, 509-512. - PubMed
-
- Benaud, C. M., and Dickson, R. B. (2001). Regulation of the expression of c-Myc by β1 integrins in epithelial cells. Oncogene 20, 759-768. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ze'ev, A., Shtutman, M., and Zhurinsky, J. (2000). The integration of cell adhesion with gene expression: the role of β-catenin. Exp. Cell Res. 261, 75-82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

