Neurokininergic mechanism within the lateral crescent nucleus of the parabrachial complex participates in the heart-rate response to nociception
- PMID: 15703395
- PMCID: PMC6725996
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4075-04.2005
Neurokininergic mechanism within the lateral crescent nucleus of the parabrachial complex participates in the heart-rate response to nociception
Abstract
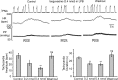
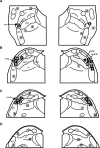
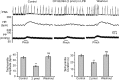
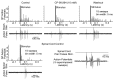
We wanted to ascertain whether the lateral parabrachial nucleus was involved in mediating the heart-rate response evoked during stimulation of somatic nociceptors. Reversible inactivation of the lateral parabrachial nucleus, using a GABA(A) agonist, reduced the reflex tachycardia evoked during noxious (mechanical) stimulation of the forelimb by approximately 50%. The same effect was observed after blockade of neurokinin 1 receptors within the lateral parabrachial nucleus, indicating a possible involvement for substance P as a neurotransmitter. Immunocytochemistry revealed a strong expression of substance P-immunoreactive fibers and boutons in all lateral subnuclei, but they were particularly dense in the lateral crescent subnucleus. Histological verification showed that the most effective injection sites for attenuating the noxious-evoked tachycardia were all placed in or near to the lateral crescent nucleus of the lateral parabrachial complex. Many single units recorded from this region were activated by high-intensity brachial nerve stimulation. The brachial nerve evoked firing responses of some of these neurons was reversibly reduced after local delivery of a neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist. However, only a minority of these neurons followed a paired-pulse stimulation protocol applied to the spinal cord, suggesting a predominance of indirect projections from the spinal cord to the parabrachial nucleus. We conclude that the cardiac component of the response to somatic nociception involves indirect spinal pathways that most likely excite neurons located in the lateral crescent nucleus of the parabrachial complex via activation of neurokinin 1 receptors.
Figures


References
-
- Abram SE, Kostreva DR, Hopp FA, Kampine JP (1983) Cardiovascular responses to noxious radiant heat in anesthetized cats. Am J Physiol 245: R576-R580. - PubMed
-
- al'Absi M, Buchanan TW, Marrero A, Lovallo WR (1999) Sex differences in pain perception and cardiovascular responses in persons with parental history for hypertension. Pain 83: 331-338. - PubMed
-
- Allen GV, Cechetto DF (1992) Functional and anatomical organization of cardiovascular pressor and depressor sites in the lateral hypothalamic area. I. Descending projections. J Comp Neurol 315: 313-332. - PubMed
-
- Bang OU, Lund A (1991) Inhibition of glutamate antagonists, MK-801 and NBQX, of cutaneo-cardiovascular pain reflex in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 203: 133-135. - PubMed
-
- Barr GA (1998) Maturation of the biphasic behavioral and heart rate response in the formalin test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60: 329-335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
