The role of the neuromodulator adenosine in alcohol's actions
- PMID: 15704350
- PMCID: PMC6826818
The role of the neuromodulator adenosine in alcohol's actions
Abstract
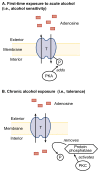
The interaction between the neuromodulator adenosine and adenosine receptors on the surface of neurons modifies the neurons' responses to neurotransmitters. The activated adenosine receptors alter the levels of small signaling molecules (i.e., second messengers) in the cells. Depending on the receptors and cells involved, these changes can make it easier or more difficult for neurotransmitters to excite the cell. Adenosine's activity is regulated by proteins called nucleoside transporters, which carry adenosine into and out of the cell. Alcohol interferes with the function of the adenosine system. For example, both acute and chronic alcohol exposure affect the function of the adenosine-carrying nucleoside transporters, thereby indirectly altering the second-messenger levels in the cells. Through this mechanism, adenosine may mediate some of alcohol's effects, such as intoxication, motor incoordination, and sedation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alcohol and neurotransmitter interactions.Alcohol Health Res World. 1997;21(2):144-8. Alcohol Health Res World. 1997. PMID: 15704351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin's role in alcohol's effects on the brain.Alcohol Health Res World. 1997;21(2):114-20. Alcohol Health Res World. 1997. PMID: 15704346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An essential role for adenosine signaling in alcohol abuse.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2010 Sep;3(3):163-74. doi: 10.2174/1874473711003030163. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2010. PMID: 21054262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol's contribution to compromised immunity.Alcohol Health Res World. 1997;21(1):30-41. Alcohol Health Res World. 1997. PMID: 15706761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerance to adenosine's accentuation of ethanol-induced motor incoordination in ethanol-tolerant mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992 Dec;16(6):1138-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1992.tb00710.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992. PMID: 1471769
Cited by
-
Alcohol: the lubricant to suicidality.Innov Clin Neurosci. 2013 Jan;10(1):20-9. Innov Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23440995 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of caffeine on alcohol consumption and nicotine self-administration in rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013 Sep;37(9):1609-17. doi: 10.1111/acer.12127. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013. PMID: 23895206 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Alcohol, Coffee, and Tobacco, Alone or in Combination, on Physiological Parameters and Anxiety in a Young Population.J Caffeine Res. 2012 Jun;2(2):70-76. doi: 10.1089/jcr.2012.0018. J Caffeine Res. 2012. PMID: 24761267 Free PMC article.
-
Partial K-Complex Recovery Following Short-Term Abstinence in Individuals with Alcohol Use Disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Aug;39(8):1417-24. doi: 10.1111/acer.12769. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 26175209 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine signaling contributes to ethanol-induced fatty liver in mice.J Clin Invest. 2009 Mar;119(3):582-94. doi: 10.1172/JCI37409. Epub 2009 Feb 16. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19221436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anwer J, Soliman MR. Ethanol-induced alterations in beta-endorphin levels in specific rat brain regions: Modulation by adenosine agonist and antagonist. Pharmacology. 1995;51:364–369. - PubMed
-
- Broad RM, Fredholm BB. A1, but not A2A, adenosine receptors modulate electrically stimulated [14C] acetylcholine release from rat cortex. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1996;277:193–197. - PubMed
-
- Carmichael FJ, Israel Y, Crawford M, Minhas K, Saldivia V, Sandrin S, Campisi P, Orrego H. Central nervous system effects of acetate: Contribution to the central effects of ethanol. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1991;259:403–408. - PubMed
-
- Coe IR, Dohrman DP, Constantinescu A, Diamond I, Gordon AS. Activation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase reverses tolerance of a nucleoside transporter to ethanol. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1996a;276:365–369. - PubMed
-
- Coe IR, Yao L, Diamond I, Gordon AS. The role of protein kinase C in cellular tolerance to ethanol. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996b;271:29468–29472. - PubMed
