Human parechovirus 3 and neonatal infections
- PMID: 15705330
- PMCID: PMC3294360
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1101.040606
Human parechovirus 3 and neonatal infections
Abstract
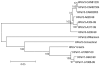
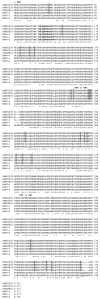
A third serotype of human parechovirus (HPeV) has been recently isolated from stool specimens of a young Japanese child with transient paralysis. We report 3 additional cases of neonatal sepsis caused by HPeV-3 in the fall of 2001 in Canadian infants 7-27 days old. All children were hospitalized with high fever, erythematous rash, and tachypnea for a median of 5 days. The viruses isolated from nasopharyngeal aspirates grew slowly on tertiary monkey kidney cells and were successfully passaged on Vero cells. The predicted amino acid identity of the VP0-VP3-VP1 region of the three viruses was 74.6%-74.8%, 73.4%-73.6%, and 97.0%-97.1% when compared to HPeV-1, -2, and -3 prototype strains, respectively. Although different, our isolates were closely related; amino acid identity was 99.6%-100% for the last 3 proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Stanway G, Hyypia T, Knowles NJ, Hovi T. Biological and molecular basis of picornavirus classification. In: Semler BL, Wimmer E, editors. Molecular biology of picornaviruses. Washington: ASM Press; 2002. p. 17–24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
