Character complexity and redundancy in writing systems over human history
- PMID: 15705551
- PMCID: PMC1634970
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2004.2942
Character complexity and redundancy in writing systems over human history
Abstract
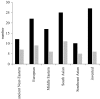
A writing system is a visual notation system wherein a repertoire of marks, or strokes, is used to build a repertoire of characters. Are there any commonalities across writing systems concerning the rules governing how strokes combine into characters; commonalities that might help us identify selection pressures on the development of written language? In an effort to answer this question we examined how strokes combine to make characters in more than 100 writing systems over human history, ranging from about 10 to 200 characters,and including numerals, abjads, abugidas, alphabets and syllabaries from five major taxa: Ancient Near-Eastern, European, Middle Eastern, South Asian, Southeast Asian. We discovered underlying similarities in two fundamental respects. (i) The number of strokes per characters is approximately three, independent of the number of characters in the writing system; numeral systems are the exception, having on average only two strokes per character. (ii) Characters are ca. 50% redundant, independent of writing system size; intuitively, this means that acharacter's identity can be determined even when half of its strokes are removed. Because writing systems are under selective pressure to have characters that are easy for the visual system to recognize and for the motor system to write, these fundamental commonalities may be a fingerprint of mechanisms underlying the visuo-motor system.
Figures



References
-
- Ager S. 1998. Omniglot: a guide to writing systems. See http://www.omniglot.com.
-
- Chakravarty I. A generalized line and junction labeling scheme with applications to scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Machine Intell. 1979;1:202–205. - PubMed
-
- Changizi M.A. Universal scaling laws for hierarchical complexity in languages, organisms, behaviors and other combinatorial systems. J. Theor. Biol. 2001;211:277–295. - PubMed
-
- Changizi M.A. The relationship between number of muscles, behavioral repertoire, and encephalization in mammals. J. Theor. Biol. 2003a;220:157–168. - PubMed
-
- Changizi M.A. Kluwer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2003b. The brain from 25000 feet: high level explorations of brain complexity, perception, induction and vagueness.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
