Lnk inhibits erythropoiesis and Epo-dependent JAK2 activation and downstream signaling pathways
- PMID: 15705783
- PMCID: PMC1894992
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-4093
Lnk inhibits erythropoiesis and Epo-dependent JAK2 activation and downstream signaling pathways
Abstract
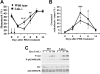
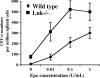
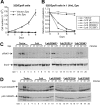
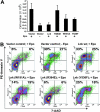
Erythropoietin (Epo), along with its receptor EpoR, is the principal regulator of red cell development. Upon Epo addition, the EpoR signaling through the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) activates multiple pathways including Stat5, phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI-3K)/Akt, and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). The adaptor protein Lnk is implicated in cytokine receptor signaling. Here, we showed that Lnk-deficient mice have elevated numbers of erythroid progenitors, and that splenic erythroid colony-forming unit (CFU-e) progenitors are hypersensitive to Epo. Lnk(-/-) mice also exhibit superior recovery after erythropoietic stress. In addition, Lnk deficiency resulted in enhanced Epo-induced signaling pathways in splenic erythroid progenitors. Conversely, Lnk overexpression inhibits Epo-induced cell growth in 32D/EpoR cells. In primary culture of fetal liver cells, Lnk overexpression inhibits Epo-dependent erythroblast differentiation and induces apoptosis. Lnk blocks 3 major signaling pathways, Stat5, Akt, and MAPK, induced by Epo in primary erythroblasts. In addition, the Lnk Src homology 2 (SH2) domain is essential for its inhibitory function, whereas the conserved tyrosine near the C-terminus and the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of Lnk are not critical. Furthermore, wild-type Lnk, but not the Lnk SH2 mutant, becomes tyrosine-phosphorylated following Epo administration and inhibits EpoR phosphorylation and JAK2 activation. Hence, Lnk, through its SH2 domain, negatively modulates EpoR signaling by attenuating JAK2 activation, and regulates Epo-mediated erythropoiesis.
Figures



References
-
- Wu H, Liu X, Jaenisch R, Lodish HF. Generation of committed erythroid BFU-E and CFU-E progenitors does not require erythropoietin or the erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1995;83: 59-67. - PubMed
-
- Socolovsky M, Constantinescu SN, Bergelson S, Sirotkin A, Lodish HF. Cytokines in hematopoiesis: specificity and redundancy in receptor function. Adv Protein Chem. 1998;52: 141-198. - PubMed
-
- Wojchowski DM, Gregory RC, Miller CP, Pandit AK, Pircher TJ. Signal transduction in the erythropoietin receptor system. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253: 143-156. - PubMed
-
- Parganas E, Wang D, Stravopodis D, et al. Jak2 is essential for signaling through a variety of cytokine receptors. Cell. 1998;93: 385-395. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer H, Cumano A, Muller M, Wu H, Huff-stadt U, Pfeffer K. Jak2 deficiency defines an essential developmental checkpoint in definitive hematopoiesis. Cell. 1998;93: 397-409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

