Light regulates COP1-mediated degradation of HFR1, a transcription factor essential for light signaling in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15705947
- PMCID: PMC1069700
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.104.030205
Light regulates COP1-mediated degradation of HFR1, a transcription factor essential for light signaling in Arabidopsis
Abstract
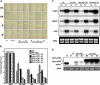
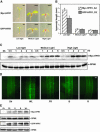
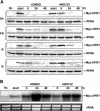
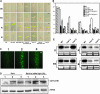
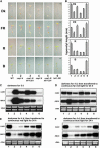
Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings undergo photomorphogenesis in the light and etiolation in the dark. Long Hypocotyl in Far-Red 1 (HFR1), a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, is required for both phytochrome A-mediated far-red and cryptochrome 1-mediated blue light signaling. Here, we report that HFR1 is a short-lived protein in darkness and is degraded through a 26S proteasome-dependent pathway. Light, irrespective of its quality, enhances HFR1 protein accumulation via promoting its stabilization. We demonstrate that HFR1 physically interacts with Constitutive Photomorphogenesis 1 (COP1) and that COP1 exhibits ubiquitin ligase activity toward HFR1 in vitro. In addition, we show that COP1 is required for degradation of HFR1 in vivo. Furthermore, plants overexpressing a C-terminal 161-amino acid fragment of HFR1 (CT161) display enhanced photomorphogenesis, suggesting an autonomous function of CT161 in promoting light signaling. This truncated HFR1 gene product is more stable than the full-length HFR1 protein in darkness, indicating that the COP1-interacting N-terminal portion of HFR1 is essential for COP1-mediated destabilization of HFR1. These results suggest that light enhances HFR1 protein accumulation by abrogating COP1-mediated degradation of HFR1, which is necessary and sufficient for promoting light signaling. Additionally, our results substantiate the E3 ligase activity of COP1 and its critical role in desensitizing light signaling.
Figures


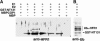


Similar articles
-
HFR1 is targeted by COP1 E3 ligase for post-translational proteolysis during phytochrome A signaling.Genes Dev. 2005 Mar 1;19(5):593-602. doi: 10.1101/gad.1247205. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15741320 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal proteasome-mediated degradation of PIFs and HFR1 underlies photomorphogenic development in Arabidopsis.Development. 2017 May 15;144(10):1831-1840. doi: 10.1242/dev.146936. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Development. 2017. PMID: 28420710 Free PMC article.
-
The degradation of HFR1, a putative bHLH class transcription factor involved in light signaling, is regulated by phosphorylation and requires COP1.Curr Biol. 2004 Dec 29;14(24):2296-301. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.12.026. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15620659
-
Constitutive photomorphogenesis protein 1 (COP1) and COP9 signalosome, evolutionarily conserved photomorphogenic proteins as possible targets of melatonin.J Pineal Res. 2016 Aug;61(1):41-51. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12340. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Pineal Res. 2016. PMID: 27121162 Review.
-
The activities of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1/SPA, a key repressor in light signaling.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017 Jun;37:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28433946 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative splicing of transcription factors in plant responses to low temperature stress: mechanisms and functions.Planta. 2013 Jun;237(6):1415-24. doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1882-4. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23624977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A PP6-type phosphatase holoenzyme directly regulates PIN phosphorylation and auxin efflux in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2012 Jun;24(6):2497-514. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.098905. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22715043 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis CSN5B interacts with VTC1 and modulates ascorbic acid synthesis.Plant Cell. 2013 Feb;25(2):625-36. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.106880. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23424245 Free PMC article.
-
A Negative Feedback Loop between PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORs and HECATE Proteins Fine-Tunes Photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2016 Apr;28(4):855-74. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00122. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 27073231 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Defense Responses to Biotic Stress and Its Interplay With Fluctuating Dark/Light Conditions.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 4;12:631810. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.631810. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33763093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad, M., Jarillo, J.A., Smirnova, O., and Cashmore, A.R. (1998). The CRY1 blue light photoreceptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro. Mol. Cell 1, 939–948. - PubMed
-
- Ang, L.-H., Chattopadhyay, S., Wei, N., Oyama, T., Okada, K., Batschauer, A., and Deng, X.W. (1998). Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol. Cell 1, 213–222. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, D., Viczián, A., Kircher, S., Nobis, T., Nitschke, R., Kunkel, T., Panigrahi, K.C.S., Ádám, E., Fejes, E., Schäfer, E., and Nagy, F. (2004). Constitutive photomorphogenesis 1 and multiple photoreceptors control degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3, a transcription factor required for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 1433–1445. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benvenuto, G., Formiggini, F., Laflamme, P., Malakhov, M., and Bowler, C. (2002). The photomorphogenesis regulator DET1 binds the amino-terminal tail of histone H2B in a nucleosome context. Curr. Biol. 12, 1529–1534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

