Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: mutations in both the CBP and EP300 genes cause disease
- PMID: 15706485
- PMCID: PMC1199295
- DOI: 10.1086/429130
Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: mutations in both the CBP and EP300 genes cause disease
Abstract
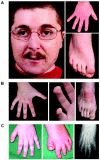
CREB-binding protein and p300 function as transcriptional coactivators in the regulation of gene expression through various signal-transduction pathways. Both are potent histone acetyl transferases. A certain level of CREB-binding protein is essential for normal development, since inactivation of one allele causes Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS). There is a direct link between loss of acetyl transferase activity and RSTS, which indicates that the disorder is caused by aberrant chromatin regulation. We screened the entire CREB-binding protein gene (CBP) for mutations in patients with RSTS by using methods that find point mutations and larger rearrangements. In 92 patients, we were able to identify a total of 36 mutations in CBP. By using multiple ligation-dependent probe amplification, we found not only several deletions but also the first reported intragenic duplication in a patient with RSTS. We extended the search for mutations to the EP300 gene and showed that mutations in EP300 also cause this disorder. These are the first mutations identified in EP300 for a congenital disorder.
Figures


References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for nucleotide sequences [accession numbers NM_004380 and NM_001429.1])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritence in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.gov/Omim/ (for RSTS)
References
-
- Alarcon JM, Malleret G, Touzani K, Vronskaya S, Ishii S, Kandel ER, Barco A (2004) Chromatin acetylation, memory, and LTP are impaired in CBP+/− mice: a model for the cognitive deficit in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and its amelioration. Neuron 42:947–959 - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T (1996) The CBP coactivator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 384:641–643 - PubMed
-
- Bartsch O, Wagner A, Hinkel GK, Krebs P, Stumm M, Schmalenberger B, Bohm S, Balci S, Majewski F (1999) FISH studies in 45 patients with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: deletions associated with polysplenia, hypoplastic left heart and death in infancy. Eur J Hum Genet 7:748–756 - PubMed
-
- Blough RI, Petrij F, Dauwerse JG, Milatovich-Cherry A, Weiss L, Saal HM, Rubinstein JH (2000) Variation in microdeletions of the cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein gene at chromosome band 16p13.3 in the Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Am J Med Genet 90:29–34 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

