Impairments of brain and behavior: the neurological effects of alcohol
- PMID: 15706764
- PMCID: PMC6826797
Impairments of brain and behavior: the neurological effects of alcohol
Abstract
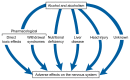
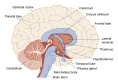
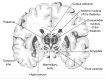
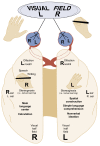
Chronic heavy drinking and alcoholism can have serious repercussions for the functioning of the entire nervous system, particularly the brain. These effects include changes in emotions and personality as well as impaired perception, learning, and memory. Neuropathological and imaging techniques have provided evidence of physical brain abnormalities in alcoholics, such as atrophy of nerve cells and brain shrinkage. At the cellular level, alcohol appears to directly affect brain function in a variety of ways, primarily by interfering with the action of glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and other neurotransmitters. Neurological disorders also can result from vitamin deficiency and liver disease, two health problems that commonly occur with alcoholism. Other hypotheses, based on factors such as aging, gender, and genetics, have been developed to explain various alcohol-related neurological consequences. Many pharmacological treatments to improve neuropsychological functioning in alcoholics have been tested, but none has proved entirely successful. With prolonged abstinence, however, slow recovery of cognitive functioning can occur in some cases.
Figures
References
-
- Babor TF, Hesselbrock V, Meyer R, Schoemaker W, editors. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1994. Types of alcoholics. Evidence from clinical, experimental, and genetic research; p. 708. - PubMed
-
- Blansjaar BA, Vielvoye GJ, van Dijk JG, Rijnders RJ. Similar brain lesions in alcoholics and Korsakoff patients: MRI, psychometric, and clinical findings. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery. 1992;94(3):197–203. - PubMed
-
- Charness ME. Brain lesions in alcoholics. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1993;17(1):2–11. - PubMed
-
- Courville CB. Effects of Alcohol on the Nervous System of Man. Los Angeles: San Lucas Press; 1966.
-
- Drake AI, Hannay HJ, Gam J. Effects of chronic alcoholism on hemispheric functioning: An examination of gender differences for cognitive and dichotic listening tasks. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 1990;12(5):781–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
