A behavioral-genetic perspective on children of alcoholics
- PMID: 15706771
- PMCID: PMC6826807
A behavioral-genetic perspective on children of alcoholics
Abstract
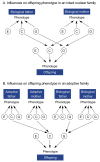
Resemblance between parents and their children with respect to certain behaviors (e.g., alcohol use) may result from shared genes or from environmental influences that affect all members of a family similarly. Behavioral geneticists have used adoption, twin, and genetic marker studies to investigate the contributions of genetic as well as shared and nonshared environmental influences to the increased risk for alcoholism in children of alcoholics (COA's). These analyses have found that in male COA's, genetic makeup (i.e., genotype) plays an important role in the development of alcoholism; in female COA's, however, the results were less consistent. Moreover, for both men and women, genetic factors alone cannot account for their risk of alcoholism. The behavioral-genetic concepts of genotype-environment interaction and genotype-environment correlation may provide useful models for the joint influences of genetic and environmental factors in the development of alcoholism.
Figures
References
-
- Bohman M, Sigvardsson S, Cloninger CR. Maternal inheritance of alcohol abuse: Cross-fostering analysis of adopted women. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1981;38:965–969. - PubMed
-
- Cadoret RJ, O’Gorman T, Troughton E, Heywood E. Alcoholism and antisocial personality: Interrelationships, genetic and environmental factors. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1985;42:161–167. - PubMed
-
- Cadoret RJ, Troughton E, O’Gorman TW. Genetic and environmental factors in alcohol abuse and antisocial personality. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1987;48:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Cloninger CR. Neurogenetic adaptive mechanisms in alcoholism. Science. 1987;236:410–416. - PubMed
-
- Cloninger CR, Bohman M, Sigvardsson S. Inheritance of alcohol abuse: Cross-fostering analysis of adopted men. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1981;38:861–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
