A developmental behavior-genetic perspective on alcoholism risk
- PMID: 15706788
- PMCID: PMC6761808
A developmental behavior-genetic perspective on alcoholism risk
Abstract
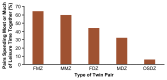
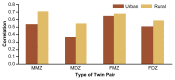
Although behavioral problems associated with abuse of alcohol emerge during late adolescence and adulthood, some behavioral characteristics indicative of an increased risk of alcoholism may already be obvious during early childhood. Studies in several countries have demonstrated that children with high levels of novelty-seeking behavior and low levels of harm-avoidance behavior are more likely to develop alcohol-related problems during adolescence. Moreover, as early as age 3, children at high risk of future alcoholism because of a family history are more active, more impatient, and more aggressive than matched controls of low-risk children. Causal influences on the initiation of drinking must be distinguished from those that affect patterns of consumption once drinking is initiated. Studies of adolescent twins have demonstrated that initiation of drinking is primarily influenced by the drinking status of parents, siblings, and friends and by socioregional differences in the environments within which adolescent twins reside. The influence of genetic factors is negligible. Conversely, once initiated, differences in frequency and quantity of drinking are strongly influenced by genetic factors. However, these influences, too, are modulated by sibling and peer effects and by regional environmental variation.
Figures
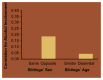
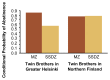
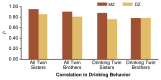
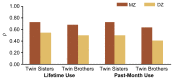
Similar articles
-
Genetic and environmental influences on the development of alcoholism: resilience vs. risk.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Dec;1094:193-201. doi: 10.1196/annals.1376.019. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17347351 Review.
-
Co-twin dependence modifies heritability of abstinence and alcohol use: a population-based study of Finnish twins.Twin Res Hum Genet. 2005 Jun;8(3):232-44. doi: 10.1375/1832427054253095. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15989750
-
Adolescent alcohol expectancies in offspring from families at high risk for developing alcoholism.J Stud Alcohol. 2001 Nov;62(6):763-72. doi: 10.15288/jsa.2001.62.763. J Stud Alcohol. 2001. PMID: 11838913
-
Drinking or abstaining at age 14? A genetic epidemiological study.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001 Nov;25(11):1594-604. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2001. PMID: 11707634
-
A behavioral-genetic perspective on children of alcoholics.Alcohol Health Res World. 1997;21(3):210-7. Alcohol Health Res World. 1997. PMID: 15706771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The genetics of alcoholism.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009 Oct;11(5):364-9. doi: 10.1007/s11920-009-0055-4. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009. PMID: 19785977 Review.
-
Time course of elevated ethanol intake in adolescent relative to adult rats under continuous, voluntary-access conditions.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007 Jul;31(7):1159-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00417.x. Epub 2007 May 20. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007. PMID: 17511750 Free PMC article.
-
FinnTwin12 Cohort: An Updated Review.Twin Res Hum Genet. 2019 Oct;22(5):302-311. doi: 10.1017/thg.2019.83. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31640839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genotype-environment correlation by intervention effects underlying middle childhood peer rejection and associations with adolescent marijuana use.Dev Psychopathol. 2022 Feb;34(1):171-182. doi: 10.1017/S0954579420001066. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Dev Psychopathol. 2022. PMID: 33349288 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gene-lifecourse interaction for alcohol consumption in adolescence and young adulthood: five monoamine genes.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007 Jun 5;144B(4):417-23. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30340. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2007. PMID: 17440951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin J, Li L, Patterson C, Greenberg BD, Murphy DL, Hamer D. Population and familial association between the D4 dopamine receptor gene and measures of novelty seeking. Nature Genetics. 1996;12:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Blum K, Noble EP, Sheridan PJ, Montgomery A, Ritchie T, Ozkaragoz T, Fitch RJ, Wood R, Finley O, Sadlack F. Genetic predisposition in alcoholism: Association of the D2 dopamine receptor TaqI B1 RFLP with severe alcoholics. Alcohol. 1993;10:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Ebstein RP, Novick O, Umansky R, Priel B, Osher Y, Blaine D, Bennett ER, Nemanov L, Katz M, Belmaker RH. Dopamine D4 receptor (D4DR) exon III polymorphisms associated with the human personality trait of novelty seeking. Nature Genetics. 1996;12:78–80. - PubMed
-
- Ebstein RP, Levine J, Geller V, Auerbach J, Gritsenko I, Belmaker RH. Dopamine D4 receptor and serotonin transporter promoter in the determination of neonatal temperament. Molecular Psychiatry. 1998;3:238–246. - PubMed
-
- Noble EP, Ozkragoz TZ, Ritchie TL, Zhang X, Belin TR, Sparkes RS. D2 and D4 dopamine receptor polymorphisms and personality. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 1998;81:257–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
