Alcohol-seeking behavior: the roles of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the endogenous opioid system
- PMID: 15706797
- PMCID: PMC6761903
Alcohol-seeking behavior: the roles of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the endogenous opioid system
Abstract
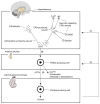
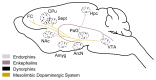
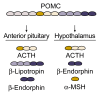
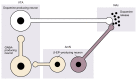
Both the hormones of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the endogenous opioid system are activated in response to stress as well as after alcohol consumption, supporting the hypothesis that stress can influence both alcohol consumption and craving for alcohoL Activation of the HPA axis by stress or alcohol results in the production of glucocorticoid hormones, such as cortisol. Those hormones, in turn, are important for the release of the brain chemical dopamine in certain brain areas that are associated with the rewarding and reinforcing effects of alcohol and other drugs. Alcohol-induced release of certain endogenous opioids similarly results in dopamine release in those brain regions. Through this mechanism, both the HPA axis and the endogenous opioid system may influence alcohol consumption. Consequently, genetically determined differences in the activities of the HPA axis and endogenous opioid system may help determine a person's alcohol consumption level and vulnerability to alcoholism.
Figures
References
-
- Akil H, Cicero TJ. Overview of the endogenous opioid systems: Anatomical, biochemical and functional issues. In: Rodgers RJ, Cooper SJ, editors. Endorphins, Opiates and Behavioural Processes. Chichester, UK: John Wiley and Sons Ltd; 1986. pp. 1–23.
-
- Benjamin D, Grant ER, Pohorecky LA. Naltrexone reverses ethanol stimulated dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of awake freely moving rats. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1992;16:617–626.
-
- Charness ME. Ethanol and opioid receptor signaling. Experientia. 1989;45:418–428. - PubMed
-
- de Wit H. Priming effects with drugs and other reinforcers. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 1996;4:5–10.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
