Age-related glutamate and glutamine concentration changes in normal human brain: 1H MR spectroscopy study at 4 T
- PMID: 15708441
- PMCID: PMC2443746
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.07.001
Age-related glutamate and glutamine concentration changes in normal human brain: 1H MR spectroscopy study at 4 T
Abstract
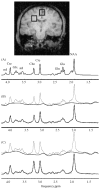
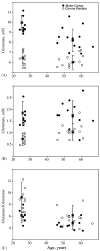
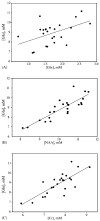
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy was performed at 4 T to determine effects of age, region and gender on glutamate and glutamine in the normal human brain. Furthermore, glutamate and glutamine alterations with age were tested for correlations with other cerebral metabolites. Two 8 cm3 volumes were selected in corona radiata and mesial motor cortex in normal subjects (N = 24) between 24 and 68 years old. Older subjects had lower glutamate concentration in the motor cortex compared to younger subjects (p < 0.001). In corona radiata, older subjects demonstrated a trend in higher glutamine compared to younger subjects (p = 0.05). Glutamate in the motor cortex was positively correlated with glutamine, N-acetyl aspartate and creatine. Reduced glutamate and N-acetyl aspartate in the motor cortex is consistent with neuronal loss/shrinkage with age. In conclusion, different patterns in association with normal aging in these brain regions were detected in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aging alters the multichemical networking profile of the human brain: an in vivo (1)H-MRS study of young versus middle-aged subjects.J Neurochem. 2001 Apr;77(1):292-303. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.t01-1-00238.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11279285 Clinical Trial.
-
Diabetes and the link between neuroplasticity and glutamate in the aging human motor cortex.Clin Neurophysiol. 2019 Sep;130(9):1502-1510. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.04.721. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31295719 Free PMC article.
-
Aging alters regional multichemical profile of the human brain: an in vivo 1H-MRS study of young versus middle-aged subjects.J Neurochem. 2001 Jan;76(2):582-93. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00026.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11208921 Clinical Trial.
-
Localized 1H-NMR spectroscopy in patients with fibromyalgia: a controlled study of changes in cerebral glutamate/glutamine, inositol, choline, and N-acetylaspartate.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):R134. doi: 10.1186/ar3072. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20609227 Free PMC article.
-
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the human brain in schizophrenia.Rev Neurosci. 2000;11(2-3):147-58. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2000.11.2-3.147. Rev Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10718151 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased glutamate concentration in the auditory cortex of persons with autism and first-degree relatives: a (1)H-MRS study.Autism Res. 2013 Feb;6(1):1-10. doi: 10.1002/aur.1260. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Autism Res. 2013. PMID: 23166003 Free PMC article.
-
Tenovin-1 Induces Senescence and Decreases Wound-Healing Activity in Cultured Rat Primary Astrocytes.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019 May 1;27(3):283-289. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2018.107. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2019. PMID: 30092626 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate-sensitive imaging and evaluation of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler. 2019 Oct;25(12):1580-1592. doi: 10.1177/1352458518799583. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Mult Scler. 2019. PMID: 30230400 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics to Study Human Aging: A Review.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(4):457-477. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230407123727. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37026499 Review.
-
Effect of age and sex differences on the abundances of neuronal, glial, and endothelial cells in non-diseased brain tissue.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 19;19(12):e0313855. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313855. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39700109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartha R, Drost DJ, Menon RS, Williamson PC. Comparison of the quantification precision of human short echo time 1H spectroscopy at 1.5 and 4.0 Tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2000;44:185–92. - PubMed
-
- Blandini F, Greenamyre JT. Protective and symptomatic strategies for therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Drugs Today (Barc) 1999;35(6):473–83. - PubMed
-
- Brand A, Richter-Landsberg C, Leibfritz D. Multinuclear NMR studies on the energy metabolism of glial and neuronal cells. Dev Neurosci. 1993;15:289–98. - PubMed
-
- Brooks JC, Roberts N, Kemp GJ, Gosney MA, Lye M, White-house GH. A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of age-related changes in frontal lobe metabolite concentrations. Cereb Cortex. 2001;11(7):598–605. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Ernst T, Poland RE, Jenden DJ. In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the normal aging human brain. Life Sci. 1996;58:2049–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

