CNI-1493, an inhibitor of proinflammatory cytokines, retards cartilage destruction in rats with collagen induced arthritis
- PMID: 15708902
- PMCID: PMC1755383
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.021550
CNI-1493, an inhibitor of proinflammatory cytokines, retards cartilage destruction in rats with collagen induced arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate if administration of CNI-1493, an inhibitor of the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines and NO, protects against development of joint destruction in collagen induced arthritis (CIA) in rats.
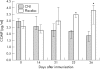
Methods: In a placebo controlled experiment, CNI-1493 was given once daily intraperitoneally after onset of clinical arthritis in DA rats. Disease progression was studied by clinical scoring of arthritis, serial measurement of serum levels of COMP, and histological examination of joints.
Results: Clinical signs of arthritis were significantly reduced in the CNI-1493 treated group of rats in comparison with the placebo treated group. Histological examinations of paws demonstrated a significant reduction of cartilage destruction in the CNI-1493 treated group, but marked destruction of cartilage in the placebo group. Serum levels of COMP increased in the placebo group, whereas in the CNI-1493 treated group levels were low and decreased significantly during the observation time.
Conclusions: Treatment with CNI-1493 provides efficient protection against synovial inflammation and cartilage destruction when used therapeutically in CIA. The protective effect against cartilage destruction can be monitored by measuring serum COMP. These observations make CNI-1493 an attractive candidate for therapeutic studies in human arthritis, and COMP an attractive serum marker for monitoring joint protective effects.
Figures

Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

