TNF receptor (TNFR)-associated factor (TRAF) 3 serves as an inhibitor of TRAF2/5-mediated activation of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway by TRAF-binding TNFRs
- PMID: 15708970
- PMCID: PMC549490
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0500187102
TNF receptor (TNFR)-associated factor (TRAF) 3 serves as an inhibitor of TRAF2/5-mediated activation of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway by TRAF-binding TNFRs
Abstract
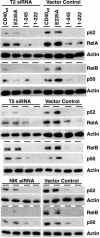
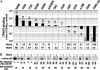
TNF family members and their receptors contribute to increased gene expression for inflammatory processes and intracellular cascades leading to programmed cell death, both via activation of NF-kappaB. TNF receptor (TNFR)-associated factors (TRAFs) are cytoplasmic adaptor proteins binding to various receptors of the TNFR family. In an attempt to delineate the role of individual TRAFs, we compared NF-kappaB activation by CD40(wt) and CD40 mutants with different TRAF recruitment patterns. Recognized only recently, NF-kappaB signaling occurs at least via two different pathways. Each pathway results in nuclear translocation of two different Reldimers, the canonical p50/RelA and the noncanonical p52/RelB. Here, we show that via TRAF6, CD40 mediates only the activation of the canonical NF-kappaB pathway. Via TRAF2/5, CD40 activates both the canonical and the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathways. We observed that TRAF3 specifically blocked the NF-kappaB activation via TRAF2/5. This inhibitory effect of TRAF3 depends on the presence of an intact zinc finger domain. Paradoxically, suppression of TRAF2/5-mediated NF-kappaB activation by TRAF3 resulted in enhanced transcriptional activity of TRAF6-mediated canonical NF-kappaB emanating from CD40. We also observed that 12 TNFR family members (p75TNFR, LTbetaR, RANK, HVEM, CD40, CD30, CD27, 4-1BB, GITR, BCMA, OX40, and TACI) are each capable of activating the alternative NF-kappaB pathway and conclude that TRAF3 serves as a negative regulator of this pathway for all tested receptors.
Figures



References
-
- Locksley, R. M., Killeen, N. & Lenardo, M. J. (2001) Cell 104, 487–501. - PubMed
-
- Rothe, M., Wong, S. C., Henzel, W. J. & Goeddel, D. V. (1994) Cell 78, 681–692. - PubMed
-
- Dempsey, P. W., Doyle, S. E., He, J. Q. & Cheng, G. (2003) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14, 193–209. - PubMed
-
- Hsu, H., Shu, H.-B., Pan, M.-G. & Goeddel, D. V. (1996) Cell 84, 299–308. - PubMed
-
- Malinin, N. L., Boldin, M. P., Kovalenko, A. V. & Wallach, D. (1997) Nature 385, 540–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

