Genome-wide annotation and expression profiling of cell cycle regulatory genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 15710686
- PMCID: PMC1065349
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.054155
Genome-wide annotation and expression profiling of cell cycle regulatory genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
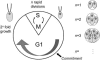
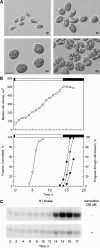
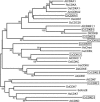
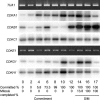
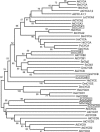
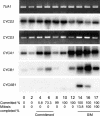
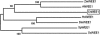
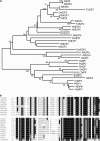
Eukaryotic cell cycles are driven by a set of regulators that have undergone lineage-specific gene loss, duplication, or divergence in different taxa. It is not known to what extent these genomic processes contribute to differences in cell cycle regulatory programs and cell division mechanisms among different taxonomic groups. We have undertaken a genome-wide characterization of the cell cycle genes encoded by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a unicellular eukaryote that is part of the green algal/land plant clade. Although Chlamydomonas cells divide by a noncanonical mechanism termed multiple fission, the cell cycle regulatory proteins from Chlamydomonas are remarkably similar to those found in higher plants and metazoans, including the proteins of the RB-E2F pathway that are absent in the fungal kingdom. Unlike in higher plants and vertebrates where cell cycle regulatory genes have undergone extensive duplication, most of the cell cycle regulators in Chlamydomonas have not. The relatively small number of cell cycle genes and growing molecular genetic toolkit position Chlamydomonas to become an important model for higher plant and metazoan cell cycles.
Figures




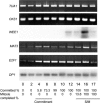
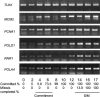
References
-
- Abrahams S, Cavet G, Oakenfull EA, Carmichael JP, Shah ZH, Soni R, Murray JAH (2001) A novel and highly divergent Arabidopsis cyclin isolated by complementation in budding yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta 1539: 1–6 - PubMed
-
- Albani D, Mariconti L, Ricagno S, Pitto L, Moroni C, Helin K, Cella R (2000) DcE2F, a functional plant E2F-like transcriptional activator from Daucus carota. J Biol Chem 275: 19258–19267 - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Bonetta L, MacAllan D, Parry D, Holder A, Dickson C, Peters G (1994) CDK6(PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3) are a distinct subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases that associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene 9: 71–79 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

