New anticoagulants: beyond heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin and warfarin
- PMID: 15711585
- PMCID: PMC1576097
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706153
New anticoagulants: beyond heparin, low-molecular-weight heparin and warfarin
Abstract
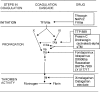
The limitations of traditional anticoagulants, heparin and warfarin, have prompted the development of new anticoagulant drugs for prevention and treatment of both venous and arterial thromboembolism. After a brief review of thrombogenesis and its regulation, this paper focuses on new anticoagulant agents in more advanced stages of clinical testing.
Figures
References
-
- ABRAHAM E., REINHART K., OPAL S., DEMEYER I., DOIG C., RODRIGUEZ A.L., BEALE R., SVOBODA P., LATERRE P.F., SIMON S., LIGHT B., SPAPEN H., STONE J., SEIBERT A., PECKELSEN C., DE DEYNE C., POSTIER R., PETTILA V., ARTIGAS A., PERCELL S.R., SHU V., ZWINGELSTEIN C., TOBIAS J., POOLE L., STOLZENBACH J.C., CREASEY A.A., OPTIMIST TRIAL STUDY GROUP Efficacy and safety of tifacogin (recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor) in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;290:238–247. - PubMed
-
- ABRAHAM E., REINHART K., SVOBODA P., SEIBERT A., OLTHOFF D., DAL NOGARE A., POSTIER R., HEMPELMANN G., BUTLER T., MARTIN E., ZWINGELSTEIN C., PERCELL S., SHU V., LEIGHTON A., CREASEY A.A. Assessment of the safety of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor in patients with severe sepsis: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blind, dose escalation study. Crit. Care Med. 2001;29:8081–8089. - PubMed
-
- AGNELLI G., BERGQVIST D., COHEN A., GALLUS A., GENT M.A randomized double-blind study to compare the efficacy and safety of fondaparinux with dalteparin in the prevention of venous thromboembolism after high-risk abdominal surgery: the Pegasus Study J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003Suppl 1Abstr. #OC006
-
- ALBERS G.W., DALEN J., LAUPACIS A., MANNING W.J., PETERSEN P., SINGER D.E. Antithrombotic therapy in atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2001;119:194S–206S. - PubMed
-
- ALEXANDER J.H., DYKE C.K., YANG H., BECKER R.C., HASSELBLAD V., ZILLMAN L.A., KLEIMAN N.S., HOCHMAN J.S., BERGER P.B., COHEN E.A., LINCOFF A.M., SAINT-JACQUES H., CHETCUTI S., BURTON J.R., BUERGLER J.M., SPENCE F.P., SHIMOTO Y., ROBERTSON T.L., KUNITADA S., BOVILL E.G., ARMSTRONG P.W., HARRINGTON R.A., The XaNADU-PCI PILOT Investigators Initial experience with factor Xa inhibition in percutaneous coronary intervention: the XaNADU-PIC Pilot. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004;2:234–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical