Neuritic regeneration and synaptic reconstruction induced by withanolide A
- PMID: 15711595
- PMCID: PMC1576076
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706122
Neuritic regeneration and synaptic reconstruction induced by withanolide A
Abstract
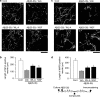
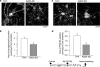
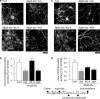
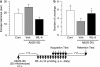
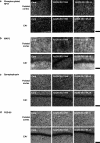
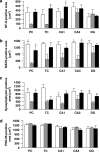
We investigated whether withanolide A (WL-A), isolated from the Indian herbal drug Ashwagandha (root of Withania somnifera), could regenerate neurites and reconstruct synapses in severely damaged neurons. We also investigated the effect of WL-A on memory-deficient mice showing neuronal atrophy and synaptic loss in the brain. Axons, dendrites, presynapses, and postsynapses were visualized by immunostaining for phosphorylated neurofilament-H (NF-H), microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), synaptophysin, and postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95), respectively. Treatment with A beta(25-35) (10 microM) induced axonal and dendritic atrophy, and pre- and postsynaptic loss in cultured rat cortical neurons. Subsequent treatment with WL-A (1 microM) induced significant regeneration of both axons and dendrites, in addition to the reconstruction of pre- and postsynapses in the neurons. WL-A (10 micromol kg(-1) day(-1), for 13 days, p.o.) recovered A beta(25-35)-induced memory deficit in mice. At that time, the decline of axons, dendrites, and synapses in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus was almost recovered. WL-A is therefore an important candidate for the therapeutic treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, as it is able to reconstruct neuronal networks.
Figures
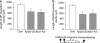

References
-
- AUDESIRK T., CABELL L., KERN M., AUDESIRK G. Estradiol influences differentiation of hippocampal neurons in vitro through an estrogen receptor-mediated process. Neuroscience. 2003;121:927–934. - PubMed
-
- BOBINSKI M., WEGIEL J., TARNAWSKI M., BOBINSKI M., REISBERG B., DE LEON M.J., MILLER D.C., WISNIEWSKI H.M. Relationships between regional neuronal loss and neurofibrillary changes in the hippocampal formation and duration and severity of Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 1997;56:414–420. - PubMed
-
- CAMBIASSO M.J., CARRER H.F. Nongenomic mechanism mediates estradiol stimulation of axon growth in male rat hypothalamic neurons in vitro. J. Neurosci. 2001;66:475–481. - PubMed
-
- CANNING D.R., MC KEON R.J., DE WITT D.A., PERRY G., WUJEK J.R., FREDERICKSON R.C., SILVER J. Amyloid of Alzheimer's disease induces reactive gliosis that inhibits axonal outgrowth. Exp. Neurol. 1993;124:289–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

