Phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit deletion and regulatory subunit deletion have opposite effects on insulin sensitivity in mice
- PMID: 15713620
- PMCID: PMC549361
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.5.1596-1607.2005
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase catalytic subunit deletion and regulatory subunit deletion have opposite effects on insulin sensitivity in mice
Abstract
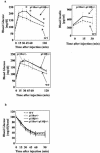
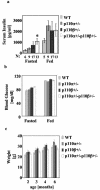
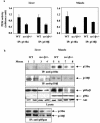
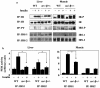
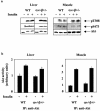
Studies ex vivo have shown that phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activity is necessary but not sufficient for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. Unexpectedly, mice lacking either of the PI3K regulatory subunits p85alpha or p85beta exhibit increased insulin sensitivity. The insulin hypersensitivity is particularly unexpected in p85alpha-/- p55alpha-/- p50alpha-/- mice, where a decrease in p110alpha and p110beta catalytic subunits was observed in insulin-sensitive tissues. These results raised the possibility that decreasing total PI3K available for stimulation by insulin might circumvent negative feedback loops that ultimately shut off insulin-dependent glucose uptake in vivo. Here we present results arguing against this explanation. We show that p110alpha+/- p110beta+/- mice exhibit mild glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia in the fasted state. Unexpectedly, p110alpha+/- p110beta+/- mice showed a approximately 50% decrease in p85 expression in liver and muscle. Consistent with this in vivo observation, knockdown of p110 by RNA interference in mammalian cells resulted in loss of p85 proteins due to decreased protein stability. We propose that insulin sensitivity is regulated by a delicate balance between p85 and p110 subunits and that p85 subunits mediate a negative role in insulin signaling independent of their role as mediators of PI3K activation.
Figures



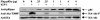

References
-
- Aguirre, V., T. Uchida, L. Yenush, R. Davis, and M. F. White. 2000. The c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J. Biol. Chem. 275:9047-9054. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre, V., E. D. Werner, J. Giraud, Y. H. Lee, S. E. Shoelson, and M. F. White. 2002. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 277:1531-1537. - PubMed
-
- Asano, T., A. Kanda, H. Katagiri, M. Nawano, T. Ogihara, K. Inukai, M. Anai, Y. Fukushima, Y. Yazaki, M. Kikuchi, R. Hooshmand-Rad, C. H. Heldin, Y. Oka, and M. Funaki. 2000. p110α is up-regulated during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells and contributes to the highly insulin-responsive glucose transport activity. J. Biol. Chem. 275:17671-17676. - PubMed
-
- Barbour, L. A., J. Shao, L. Qiao, W. Leitner, M. Anderson, J. E. Friedman, and B. Draznin. 2004. Human placental growth hormone increases expression of the p85 regulatory unit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and triggers severe insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 145:1144-1150. - PubMed
-
- Barroso, I., J. Luan, R. P. Middelberg, A. H. Harding, P. W. Franks, R. W. Jakes, D. Clayton, A. J. Schafer, S. O'Rahilly, and N. J. Wareham. 2003. Candidate gene association study in type 2 diabetes indicates a role for genes involved in beta-cell function as well as insulin action. PLoS Biol. 1:E20. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
