ZENON, a novel POZ Kruppel-like DNA binding protein associated with differentiation and/or survival of late postmitotic neurons
- PMID: 15713629
- PMCID: PMC549352
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.5.1713-1729.2005
ZENON, a novel POZ Kruppel-like DNA binding protein associated with differentiation and/or survival of late postmitotic neurons
Abstract
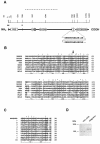
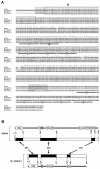
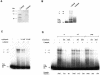
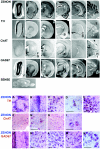
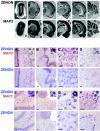
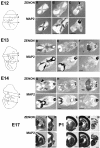
The rat tyrosine hydroxylase gene promoter contains an E-box/dyad motif and an octameric and heptameric element that may be recognized by classes of transcription factors highly expressed during nervous system development. In a one-hybrid genetic screen, we used these sites as targets to isolate cDNAs encoding new transcription factors present in the brain. We identified ZENON, a novel rat POZ protein that contains two clusters of Kruppel-like zinc fingers and that presents several features of a transcription factor. ZENON is found in nuclei following transient transfection with the cDNA. The N-terminal zinc finger cluster contains a DNA binding domain that interacts with the E box. Cotranfection experiments revealed that ZENON induces tyrosine hydroxylase promoter activity. Unlike other POZ proteins, the ZENON POZ domain is not required for either activation of transcription or self-association. In the embryonic neural tube, ZENON expression is restricted to neurons that have already achieved mitosis and are engaged in late stages of neuronal differentiation (late postmitotic neurons). ZENON neuronal expression persists in the adult brain; therefore, ZENON can be considered a marker of mature neurons. We propose that ZENON is involved in the maintenance of panneuronal features and/or in the survival of mature neurons.
Figures




References
-
- Albagli, O., P. Dhordain, C. Deweindt, G. Lecocq, and D. Leprince. 1995. The BTB/POZ domain: a new protein-protein interaction motif common to DNA- and actin-binding proteins. Cell Growth Differ. 6:1193-1198. - PubMed
-
- Albagli-Curiel, O. 2003. Ambivalent role of BCL6 in cell survival and transformation. Oncogene 22:507-516. - PubMed
-
- Albanèse, V., N. F. Biguet, H. Kiefer, E. Bayard, J. Mallet, and R. Meloni. 2001. Quantitative effects on gene silencing by allelic variation at a tetranucleotide microsatellite. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10:1785-1792. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
