Visuospatial and numerical cognitive deficits in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome
- PMID: 15714897
- PMCID: PMC4318636
- DOI: 10.1016/s0010-9452(08)70889-x
Visuospatial and numerical cognitive deficits in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome
Abstract
This article presents some of the earliest evidence of visuospatial and numerical cognitive deficits in children with the chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome; a common but ill-understood genetic disorder resulting in medical complications, cognitive impairment, and brain morphologic changes. Relative to a group of typically developing controls, deleted children performed more poorly on tests of visual attentional orienting, visual enumeration and relative numerical magnitude judgment. Results showed that performance deficits in children with the deletion could not be explained by a global deficit in psychomotor speed. Instead, our findings are supportive of the hypothesis that visuospatial and numerical deficits in children with the chromosome 22q11.2 deletion are due, at least in part, to posterior parietal dysfunction.
Figures

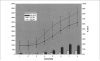
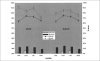
Similar articles
-
A new account of the neurocognitive foundations of impairments in space, time and number processing in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome.Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2008;14(1):52-8. doi: 10.1002/ddrr.8. Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 18612330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multilevel analysis of cognitive dysfunction and psychopathology associated with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome in children.Dev Psychopathol. 2005 Summer;17(3):753-84. doi: 10.1017/S0954579405050364. Dev Psychopathol. 2005. PMID: 16262991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overlapping numerical cognition impairments in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion or Turner syndromes.Neuropsychologia. 2008 Jan 15;46(1):82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.08.016. Epub 2007 Aug 26. Neuropsychologia. 2008. PMID: 17920087 Free PMC article.
-
[Chromosome 22q11 deletion syndrome and its relevance for child and adolescent psychiatry. An overview of etiology, physical symptoms, aspects of child development and psychiatric disorders].Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2004 May;32(2):107-15. doi: 10.1024/1422-4917.32.2.107. Z Kinder Jugendpsychiatr Psychother. 2004. PMID: 15181786 Review. German.
-
A comprehensive analysis of 22q11 gene expression in the developing and adult brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Nov 25;100(24):14433-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2235651100. Epub 2003 Nov 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14614146 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparing the broad socio-cognitive profile of youth with Williams syndrome and 22q11.2 deletion syndrome.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2017 Dec;61(12):1083-1093. doi: 10.1111/jir.12424. Epub 2017 Oct 8. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2017. PMID: 28990288 Free PMC article.
-
Catechol-O-methyltransferase polymorphism modulates cognitive control in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2009 Mar;9(1):83-90. doi: 10.3758/CABN.9.1.83. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19246329 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic copy number variants, cognition and psychosis: a meta-analysis and a family study.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Sep;26(9):5307-5319. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0820-7. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 32719466 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic sister-disorders of neurodevelopment: an evolutionary approach.Evol Appl. 2009 Feb;2(1):81-100. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-4571.2008.00056.x. Epub 2009 Jan 7. Evol Appl. 2009. PMID: 25567849 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of facial emotion expressions and perceptual processes in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome.Early Interv Psychiatry. 2023 Jan;17(1):76-84. doi: 10.1111/eip.13295. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 35347860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bearden CE, Woodin MF, Wang PP, Moss E, McDonald-McGinn D, Zackai E, Emannuel B, Cannon TD. The neurocognitive phenotype of the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: Selective deficit in visual-spatial memory. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. 2001;23:447–64. - PubMed
-
- Bellinger DC, Jonas RA, Rappaport LA, Wypij D, Wernovsky G, Kuban KCK, Barnes PD, Holmes GL, Hickey PR, Strand RD, Walsh AZ, Helmers SL, Constantinou JE, Carrazana EJ, Mayer JE, Hanley FL, Casteneda AR, Ware JH, Newburger JW. Developmental and neurologic status of children after heart surgery with hypothermic circulatory arrest or low-flow cardiopulmonary bypass. New England Journal of Medicine. 1995;332:549–555. - PubMed
-
- Bellugi U, Lichtenberger L, Jones W, Lai Z, St. George M. The neurocognitive profile of Williams syndrome: A complex pattern of strengths and weaknesses. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2000;12:7–29. - PubMed
-
- Bellugi U, Lichtenberger L, Mills D, Galaburda A, Korenberg JR. Bridging cognition, the brain and molecular genetics: Evidence from Williams syndrome. Trends in Neuroscience. 1999;22:197–207. - PubMed
-
- Bennetto L, Pennington BF. The neuropsychology of fragile x syndrome. In: Hagerman RJ, Cronister A, editors. Fragile X Syndrome: Diagnosis, Treatment and Research. Johns Hopkins University Press; Baltimore: 1996. pp. 210–248.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

