Characterization of the inactivation of rat fatty acid synthase by C75: inhibition of partial reactions and protection by substrates
- PMID: 15715522
- PMCID: PMC1183470
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041963
Characterization of the inactivation of rat fatty acid synthase by C75: inhibition of partial reactions and protection by substrates
Abstract
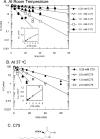
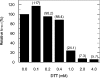
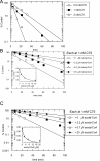
C75, a synthetic inhibitor of FAS (fatty acid synthase), has both anti-tumour and anti-obesity properties. In this study we provide a detailed kinetic characterization of the mechanism of in vitro inhibition of rat liver FAS. At room temperature, C75 is a competitive irreversible inhibitor of the overall reaction with regard to all three substrates, i.e. acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH, exhibiting pseudo-first-order kinetics of the complexing type, i.e. a weak non-covalent enzyme-inhibitor complex is formed before irreversible enzyme modification. C75 is a relatively inefficient inactivator of FAS, with a maximal rate of inactivation of 1 min(-1) and an extrapolated K(I) (dissociation constant for the initial complex) of approx. 16 mM. The apparent second-order rate constants calculated from these values are 0.06 mM(-1).min(-1) at room temperature and 0.21 mM(-1).min(-1) at 37 degrees C. We also provide experimental evidence that C75 inactivates the beta-ketoacyl synthase (3-oxoacyl synthase) partial activity of FAS. Unexpectedly, C75 also inactivates the enoyl reductase and thioesterase partial activities of FAS with about the same rates as for inactivation of the beta-ketoacyl synthase. In contrast with the overall reaction, the beta-ketoacyl synthase activity and the enoyl reductase activity, substrates do not protect the thioesterase activity of rat liver FAS from inactivation by C75. These results differentiate inactivation by C75 from that by cerulenin, which only inactivates the beta-ketoacyl synthase activity of FAS, by forming an adduct with an active-site cysteine. Interference by dithiothreitol and protection by the substrates, acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA and NADPH, further distinguish the mechanism of C75-mediated inactivation from that of cerulenin. The most likely explanation for the multiple effects observed with C75 on rat liver FAS and its partial reactions is that there are multiple sites of interaction between C75 and FAS.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Green tea epigallocatechin gallate: a natural inhibitor of fatty-acid synthase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Nov 16;288(5):1200-6. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5923. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11700039
-
Fatty acid synthase inhibition triggers apoptosis during S phase in human cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2003 Nov 1;63(21):7330-7. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14612531
-
Novel effect of C75 on carnitine palmitoyltransferase I activity and palmitate oxidation.Biochemistry. 2006 Apr 11;45(14):4339-50. doi: 10.1021/bi052186q. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16584169
-
Fatty acid metabolism as a target for obesity treatment.Physiol Behav. 2005 May 19;85(1):25-35. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.04.014. Physiol Behav. 2005. PMID: 15878185 Review.
-
Regulation of food intake and energy expenditure by hypothalamic malonyl-CoA.Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Sep;32 Suppl 4:S49-54. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.123. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. PMID: 18719599 Review.
Cited by
-
Fatty Acid Synthase Contributes to Restimulation-Induced Cell Death of Human CD4 T Cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2019 Oct 15;6:106. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00106. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31681794 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Energy Metabolism in Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 16;23(10):5572. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105572. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty acid synthase as a factor required for exercise-induced cognitive enhancement and dentate gyrus cellular proliferation.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 5;8(11):e77845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077845. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223732 Free PMC article.
-
The fatty acid synthase inhibitor triclosan: repurposing an anti-microbial agent for targeting prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2014 Oct 15;5(19):9362-81. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2433. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25313139 Free PMC article.
-
Luminal fructose inhibits rat intestinal sodium-phosphate cotransporter gene expression and phosphate uptake.Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Apr;87(4):1028-38. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.4.1028. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008. PMID: 18400728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wakil S. J. Fatty acid synthase, a proficient multifunctional enzyme. Biochemistry. 1989;28:4523–4530. - PubMed
-
- Smith S., Witkowski A., Joshi A. K. Structure and functional organization of the animal fatty acid synthase. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003;42:289–317. - PubMed
-
- Pizer E. S., Thupari J., Han W. F., Pinn M. L., Chrest F. J., Frehywot G. L., Townsend C. A., Kuhajda F. P. Malonyl-coenzyme-A is a potential mediator of cytotoxicity induced by fatty-acid synthase inhibition in human breast cancer cells and xenografts. Cancer Res. 2000;60:213–218. - PubMed
-
- Loftus T. M., Jaworsky D. E., Frehywot G. L., Townsend C. A., Ronnett G. V., Lane M. D., Kuhajda F. P. Reduced food intake and body weight in mice treated with fatty acid synthase inhibitors. Science. 2000;288:2379–2381. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

