mRNA sequence features that contribute to translational regulation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15716313
- PMCID: PMC549406
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki240
mRNA sequence features that contribute to translational regulation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
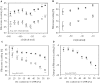
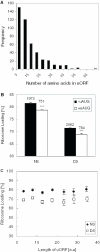
DNA microarrays were used to evaluate the regulation of the proportion of individual mRNA species in polysomal complexes in leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana under control growth conditions and following a mild dehydration stress (DS). The analysis determined that the percentage of an individual gene transcript in polysomes (ribosome loading) ranged from over 95 to <5%. DS caused a decrease in ribosome loading from 82 to 72%, with maintained polysome association for over 60% of the mRNAs with an increased abundance. To identify sequence features responsible for translational regulation, ribosome loading values and features of full-length mRNA sequences were compared. mRNAs with extreme length or high GU content in the 5'-untranslated regions (5'-UTRs) were generally poorly translated. Under DS, mRNAs with both a high GC content in the 5'-UTR and long open reading frame showed a significant impairment in ribosome loading. Evaluation of initiation A+1UG codon context revealed distinctions in the frequency of adenine in nucleotides -10 to -1 (especially at -4 and -3) in mRNAs with different ribosome loading values. Notably, the mRNA features that contribute to translational regulation could not fully explain the variation in ribosome loading, indicating that additional factors contribute to translational regulation in Arabidopsis.
Figures




References
-
- Carter M.S., Kuhn K.M., Sarnow P. Cellular internal ribosome entry site elements and the use of cDNA microarrays in their investigation. In: Sonenberg N., Hershey J.W.B., Mathews M.B., editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2000. pp. 615–635.
-
- Diehn M., Eisen M.B., Botstein D., Brown P.O. Large-scale identification of secreted and membrane-associated gene products using DNA microarrays. Nature Genet. 2000;25:58–62. - PubMed
-
- Grolleau A., Bowman J., Pradet-Balade B., Puravs E., Hanash S., Garcia-Sanz J.A., Beretta L. Global and specific translational control by rapamycin in T cells uncovered by microarrays and proteomics. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:22175–22184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

