Dopamine supersensitivity correlates with D2High states, implying many paths to psychosis
- PMID: 15716360
- PMCID: PMC548961
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409766102
Dopamine supersensitivity correlates with D2High states, implying many paths to psychosis
Abstract
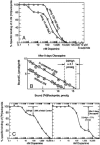
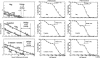
Dopamine supersensitivity occurs in schizophrenia and other psychoses, and after hippocampal lesions, antipsychotics, ethanol, amphetamine, phencyclidine, gene knockouts of Dbh (dopamine beta-hydroxylase), Drd4 receptors, Gprk6 (G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6), Comt (catechol-O-methyltransferase), or Th-/-, DbhTh/+ (tyrosine hydroxylase), and in rats born by Cesarean-section. The functional state of D2, or the high-affinity state for dopamine (D2High), was measured in these supersensitive animal brain striata. Increased levels and higher proportions (40-900%) for D2High were found in all these tissues. If many types of brain impairment cause dopamine behavioral supersensitivity and a common increase in D2High states, it suggests that there are many pathways to psychosis, any one of which can be disrupted.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

