Activity-dependent long-term potentiation of intrinsic excitability in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 15716411
- PMCID: PMC6725941
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4217-04.2005
Activity-dependent long-term potentiation of intrinsic excitability in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
Abstract
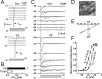
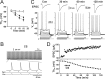
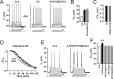
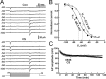
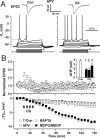
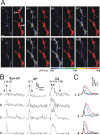
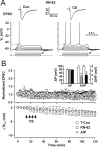
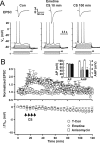
The efficiency of neural circuits is enhanced not only by increasing synaptic strength but also by increasing intrinsic excitability. In contrast to the detailed analysis of long-term potentiation (LTP), less attention has been given to activity-dependent changes in the intrinsic neuronal excitability. By stimulating hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons with synaptic inputs correlating with postsynaptic neuronal spikes, we elicited an LTP of intrinsic excitability (LTP-IE) concurring with synaptic LTP. LTP-IE was manifested as a decrease in the action potential threshold that was attributable to a hyperpolarized shift in the activation curve of voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) rather than activity-dependent changes in synaptic inputs or A-type K+ channels. Cell-attached patch recording of VGSC activities indicated such an activity-dependent change in VGSCs. Induction of LTP-IE was blocked by the NMDA receptor antagonist APV, intracellular BAPTA, the CaM kinase inhibitors KN-62 and autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide, and the protein synthesis inhibitors emetine and anisomycin. The results suggest that induction of LTP-IE shares a similar signaling pathway with the late phase of synaptic LTP and requires activation of the NMDA glutamate receptor subtype, Ca2+ influx, activity of CaM kinase II, and function of the protein synthesis. This new form of hippocampal neuronal plasticity could be a cellular correlate of learning and memory besides synaptic LTP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transient removal of extracellular Mg(2+) elicits persistent suppression of LTP at hippocampal CA1 synapses via PKC activation.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Sep;84(3):1279-88. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.3.1279. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10980002
-
Dopamine D1/5 receptor-mediated long-term potentiation of intrinsic excitability in rat prefrontal cortical neurons: Ca2+-dependent intracellular signaling.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Mar;97(3):2448-64. doi: 10.1152/jn.00317.2006. Epub 2007 Jan 17. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17229830
-
Input- and subunit-specific AMPA receptor trafficking underlying long-term potentiation at hippocampal CA3 synapses.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Jul;20(1):101-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03461.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15245483
-
CaM kinase II in long-term potentiation.Neurochem Int. 1996 Apr;28(4):343-58. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(95)00097-6. Neurochem Int. 1996. PMID: 8740440 Review.
-
Expression mechanisms underlying NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Apr 30;868:515-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb11320.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10414328 Review.
Cited by
-
Matrix Metalloprotease 3 Activity Supports Hippocampal EPSP-to-Spike Plasticity Following Patterned Neuronal Activity via the Regulation of NMDAR Function and Calcium Flux.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;54(1):804-816. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9970-7. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27351676 Free PMC article.
-
Short trains of theta frequency stimulation enhance CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability in the absence of synaptic potentiation.J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 9;29(36):11203-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1450-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19741127 Free PMC article.
-
CaMK modulates sensory neural activity to control longevity and proteostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 20;122(20):e2423428122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2423428122. Epub 2025 May 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40359038
-
It Is All in the Right Amygdala: Increased Synaptic Plasticity and Perineuronal Nets in Male, But Not Female, Juvenile Rat Pups after Exposure to Early-Life Stress.J Neurosci. 2020 Oct 21;40(43):8276-8291. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1029-20.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32978287 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic DNA methylation regulates neuronal intrinsic membrane excitability.Sci Signal. 2016 Aug 23;9(442):ra83. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf5642. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27555660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel T, Nguyen PV, Barad M, Deuel TA, Kandel ER, Bourtchouladze R (1997) Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 88: 615-626. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman CD, Linden DJ (2000) Rapid, synaptically driven increases in the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar deep nuclear neurons. Nat Neurosci 3: 109-111. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman CD, Akerman CJ, Jensen KR, Cline HT (2003) Visually driven regulation of intrinsic neuronal excitability improves stimulus detection in vivo. Neuron 39: 831-842. - PubMed
-
- Alkon DL, Sakakibara M, Forman R, Harrigan J, Lederhendler I, Farley J (1985) Reduction of two voltage-dependent K+ currents mediates retention of a learned association. Behav Neural Biol 44: 278-300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
