Toll-like receptor 4 on nonhematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines
- PMID: 15716415
- PMCID: PMC6725921
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4268-04.2005
Toll-like receptor 4 on nonhematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines
Abstract
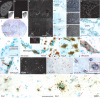
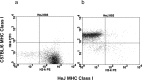
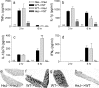
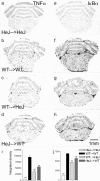
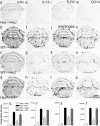
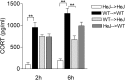
Inflammatory agonists such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induce robust systemic as well as CNS responses after peripheral administration. Responses in the innate immune system require triggering of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), but the origin of CNS sequelas has been controversial. We demonstrate expression of TLR4 transcripts in mouse brain in the meninges, ventricular ependyma, circumventricular organs, along the vasculature, and in parenchymal microglia. The contribution of TLR4 expressed in CNS resident versus hematopoietic cells to the development of CNS inflammation was examined using chimeric mice. Reciprocal bone marrow chimeras between wild-type and TLR4 mutant mice show that TLR4 on CNS resident cells is critically required for sustained inflammation in the brain after systemic LPS administration. Hematopoietic TLR4 alone supported the systemic release of acute phase cytokines, but transcription of proinflammatory genes in the CNS was reduced in duration. In contrast, TLR4 function in radiation-resistant cells was sufficient for inflammatory progression in the brains of chimeric mice, despite the striking absence of cytokine elevations in serum. Surprisingly, a temporal rise in serum corticosterone was also dependent on TLR4 signaling in nonhematopoietic cells. Our findings demonstrate a requirement for TLR4 function in CNS-resident cells, independent of systemic cytokine effects, for sustained CNS-specific inflammation and corticosterone rise during endotoxemia.
Figures

Comment in
-
The toll receptor family: from microbial recognition to seizures.Epilepsy Curr. 2006 Jan-Feb;6(1):11-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2005.00080.x. Epilepsy Curr. 2006. PMID: 16477316 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adams DH, Hanson GR, Keefe KA (2000) Cocaine and methamphetamine differentially affect opioid peptide mRNA expression in the striatum. J Neurochem 75: 2061-2070. - PubMed
-
- Berkenbosch F, van Oers J, del Rey A, Tilders F, Besedovsky H (1987) Corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the rat activated by interleukin-1. Science 238: 524-526. - PubMed
-
- Breder CD, Saper CB (1996) Expression of inducible cyclooxygenase mRNA in the mouse brain after systemic administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Brain Res 713: 64-69. - PubMed
-
- Bsibsi M, Ravid R, Gveric D, van Noort JM (2002) Broad expression of Toll-like receptors in the human central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61: 1013-1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
