Eae19, a new locus on rat chromosome 15 regulating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 15716504
- PMCID: PMC1449709
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.035261
Eae19, a new locus on rat chromosome 15 regulating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
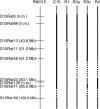
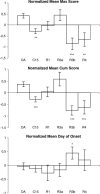
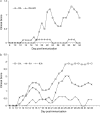
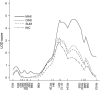
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (MOG-EAE), share a complex genetic predisposition with contributions from the major histocompatibility complex class II genes and many other genes. Linkage mapping in F(2) crosses between the susceptible DA rat strain and the resistant ACI or BN rat strains in various models of autoimmune neuroinflammation have repeatedly displayed suggestive linkage to a region on rat chromosome 15. A direct study of this region was undertaken in congenic strains by transferring resistant ACI alleles to the susceptible DA background. Phenotypic analysis demonstrated lower maximal and cumulative EAE scores in the DA.ACI-D15Rat6-D15Rat71 (C15), DA.ACI-D15Rat6-D15Rat48, D15Rat126-D15Rat71 (C15R3b), and DA.ACI-D15Rat23-D15rat71 (C15R4) strains compared to the parental DA rat strain. Linkage analysis was then performed in a (DA x PVG.AV1)F(7) advanced intercross line, resulting in a LOD score of 4.7 for the maximal EAE score phenotype at the peak marker D15Rat71 and a confidence interval of 13 Mb, overlapping with the congenic fragment defined by the C15R3b and the C15R4 strains. Thus, a new MOG-EAE locus with the designation Eae19 is identified on rat chromosome 15. There are 32 confirmed or predicted genes in the confidence interval, including immune-responsive gene 1 and neuronal ceroid lipofuscinose gene 5. Definition of loci such as Eae19 enables the characterization of genetically regulated, evolutionary conserved disease pathways in complex neuroinflammatory diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linkage analysis of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the rat identifies a locus controlling demyelination on chromosome 18.Hum Mol Genet. 1999 Nov;8(12):2183-90. doi: 10.1093/hmg/8.12.2183. Hum Mol Genet. 1999. PMID: 10545597
-
Advanced intercross line mapping of Eae5 reveals Ncf-1 and CLDN4 as candidate genes for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2006 May 15;176(10):6055-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.10.6055. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16670314
-
Genome-wide linkage analysis of chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the rat identifies a major susceptibility locus on chromosome 9.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 1;162(5):2581-8. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10072499
-
Genetics of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2004 Sep-Oct;52(5):316-25. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2004. PMID: 15507872 Review.
-
Genetics of rat neuroinflammation.J Neuroimmunol. 2000 Jul 24;107(2):191-200. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(00)00224-1. J Neuroimmunol. 2000. PMID: 10854656 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying genes for neurobehavioural traits in rodents: progress and pitfalls.Dis Model Mech. 2017 Apr 1;10(4):373-383. doi: 10.1242/dmm.027789. Dis Model Mech. 2017. PMID: 28381599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing and transcriptome profiling of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis using genome-wide exon arrays.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 10;4(11):e7773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007773. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19915720 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of candidate risk gene variations by whole-genome sequence analysis of four rat strains commonly used in inflammation research.BMC Genomics. 2014 May 21;15(1):391. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-391. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24885425 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling as a tool for positional cloning of genes-shortcut or the longest way round.Curr Genomics. 2008 Nov;9(7):494-9. doi: 10.2174/138920208786241180. Curr Genomics. 2008. PMID: 19506738 Free PMC article.
-
Combining genetic mapping with genome-wide expression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis highlights a gene network enriched for T cell functions and candidate genes regulating autoimmunity.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Dec 15;22(24):4952-66. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt343. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23900079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelmann, M., J. Wood, I. Benzel, P. Fiori, H. Lassmann et al., 1995. The N-terminal domain of the myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) induces acute demyelinating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. J. Neuroimmunol. 63: 17–27. - PubMed
-
- Akesson, E., A. Oturai, A. Svejgaard, P. Holmans, A. Compston et al., 2002. A genome-wide screen for linkage in Nordic sib-pairs with multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun. 3: 279–285. - PubMed
-
- Ban, M., G. Stewart, B. Bennetts, R. Heard, R. Simmons et al., 2002. A genome screen for linkage in Australian sibling-pairs with multiple sclerosis. Genes Immun. 3: 464–469. - PubMed
-
- Becanovic, K., L. Backdahl, E. Wallstrom, F. Aboul-Enein, H. Lassmann et al., 2003. Paradoxical effects of arthritis-regulating chromosome 4 regions on myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced encephalomyelitis in congenic rats. Eur. J. Immunol. 33: 1907–1916. - PubMed
-
- Becanovic, K., M. Jagodic, E. Wallstrom and T. Olsson, 2004. Current gene mapping strategies in experimental models of multiple sclerosis. Scand. J. Immunol. 60: 39–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

