Occupational asthma and rhinitis induced by a herbal medicine, Wonji (Polygala tenuifolia)
- PMID: 15716601
- PMCID: PMC2808574
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.1.46
Occupational asthma and rhinitis induced by a herbal medicine, Wonji (Polygala tenuifolia)
Abstract
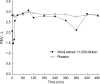
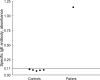
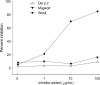
Occupational asthma is induced by many agents, including herbal materials, that are exposed in working places. Although there are a few case reports for occupational allergy induced by herbal materials, there is none for that induced by Wonji (Polygala tenuifolia). This study was conducted to evaluate clinical characteristics and immunologic mechanism of Wonji-induced asthma in a exposed-worker. A patient who complained of asthma and rhinitis symptoms, and who had worked in a herbal manufacturing factory for 8 yr, underwent a skin prick test with crude extract of Wonji under the impression of occupational asthma induced by the agent. The patient had a strong positive response to the extract on the skin prick test. Allergen bronchial challenge to the extract demonstrated a typical dual response. Serum specific IgE level to the extract was higher in the patient than in healthy controls, and ELISA inhibition test revealed complete inhibition of IgE binding with the extract, but no inhibition with Der p 2 or mugwort extracts. Six IgE binding components to the extract (10, 25, 28, 36, 50, and 90 kDa) were detected using SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis. These findings suggest that Polygala tenuifolia, a herbal material, can induce IgE-mediated bronchoconstriction in exposed workers.
Figures
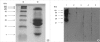
Similar articles
-
Occupational asthma and rhinitis caused by multiple herbal agents in a pharmacist.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001 Apr;86(4):469-74. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62498-2. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11345295
-
Sensitization to Empynase(pronase B) in exposed hospital personnel and identification of the Empynase allergen.Clin Exp Allergy. 2006 Mar;36(3):352-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02434.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16499647
-
Occupational rhinitis and bronchial asthma due to artichoke (Cynara scolymus).Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003 Jul;91(1):92-5. doi: 10.1016/s1081-1206(10)62066-2. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12877457
-
New occupational allergen in citrus farmers: citrus red mite (Panonychus citri).Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1999 Feb;82(2):223-8. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62601-4. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10071529
-
Preparation, structural characteristics and pharmacological activity of polysaccharides from Polygala tenuifolia: A review.Carbohydr Res. 2024 May;539:109117. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2024.109117. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Carbohydr Res. 2024. PMID: 38626569 Review.
Cited by
-
Korean ginseng-induced occupational asthma and determination of IgE binding components.J Korean Med Sci. 2008 Apr;23(2):232-5. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.2.232. J Korean Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 18437005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park HS, Kim MJ, Moon HB. Occupational asthma caused by two herb materials, Dioscorea batatas and Pinellia ternata. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994;24:575–581. - PubMed
-
- Lee SK, Cho HK, Cho SH, Kim SS, Nahm DH, Park HS. Occupational asthma and rhinitis caused by multiple herbal agents in a pharmacist. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001;86:469–474. - PubMed
-
- Kim SH, Jeong H, Kim YK, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. IgE-mediated occupational asthma induced by herbal medicine, Banha (Pinellia ternate) Clin Exp Allergy. 2001;31:779–781. - PubMed
-
- Cartier A, Malo JL, Labrecque M. Occupational asthma due to liquorice roots. Allergy. 2002;57:863. - PubMed
-
- Subiza J, Subiza JL, Escribano PM, Hinojosa M, Garcia R, Jerez M, Subiza E. Occupational asthma caused by Brazil ginseng dust. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991;88:731–736. - PubMed

